PROPERTIES OF PARALLELOGRAM WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
Find each measure in parallelogram
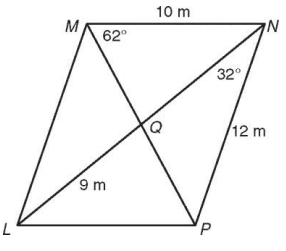
Find,
1) ML 2) LP 3) ∠LPM 4) ∠MLN 5) LN 6) QN
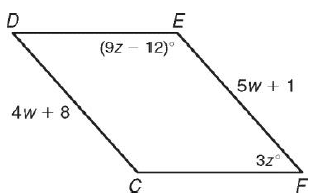
Problem 2 :
CDEF is a parallelogram. Find each measure.
(i) CD (ii) EF (iii) ∠E (iv) ∠F
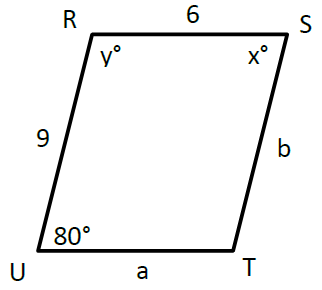
Problem 3 :
Quadrilateral RSTU is a parallelogram. Find the values of x, y, a, and b.
Problem 4 :
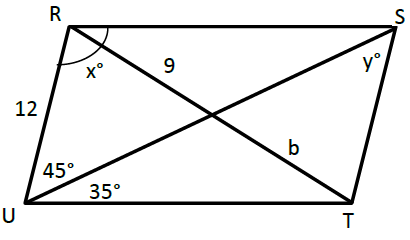
Problem 5 :
Find the missing measurements of parallelogram.
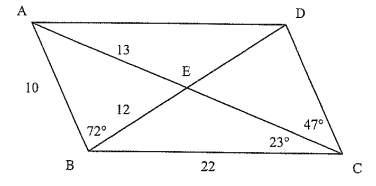
Find the measures of
|
1) CD 2) AC 3) CE 4) DA 5) DB 6) DE 7) ∠ABC 8) ∠BCD 9) ∠BAD 10) ∠DAE |
11) ∠BCD 12) ∠BCE 13) ∠ADC 14) ∠CDE 15) ∠EAB 16) ∠CED 17) ∠EDA 18) ∠AEB 19) ∠DEA |
Problem 6 :
In the figure given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. Find the values of x, y, z and p.
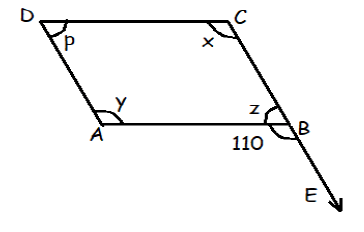
Problem 7 :
State whether each statement is always, sometimes, or never true for a parallelogram. Explain your reasoning.
a. The opposite sides are congruent.
b. All four sides are congruent.
c. The diagonals are congruent.
d. The opposite angles are congruent.
e. The adjacent angles are congruent.
f. The adjacent angles are complementary
Answer Key
|
1) ML = 12 m, 2) LP = 10 m 3) ∠LPM = 62° |
4) ∠MLN = 32° 5) LN = 18 6) QN = 9 m |
2) (i) CD = 36 (ii) EF = 36 (iii) ∠E = 132 (iv) ∠F = 48
3) x = 80°, y = 100, a = 6 and b = 9
4) x = 100, y = 45 and b = 9
5)
|
1) CD = 10 2) AC = 26 3) CE = 13 4) DA = 22 5) DB = 24 6) DE = 12 7) ∠ABC = 110 8) ∠BCD = 70 9) ∠BAD = 70 10) ∠DAE = 23 |
11) ∠BEC = 119 12) ∠BCE = 23 13) ∠ADC = 110 14) ∠CDE = 72 15) ∠EAB = 47 16) ∠CED = 61 17) ∠EDA = 38 18) ∠AEB = 61 19) ∠DEA = 119 |
6) x = 110 and p = 70
7)
a. In parallelogram, always opposite sides will be congruent.
b. In parallelogram, sometimes all four sides will be congruent. Then it is rhombus.
c. In parallelogram, sometimes the diagonals are congruent.
d. The opposite angles are congruent always.
e. Sometimes the adjacent angles are congruent. When adjacent angles are equal, its measure must be 90 degree, then that shape is known as rectangle.
f. The adjacent angles will never be complementary, because the sum of adjacent angles must be add up to 180 degree.
Problem 1 :
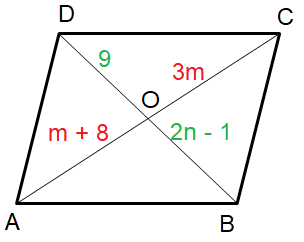
For the parallelogram given below, solve for m and n.
Problem 2 :
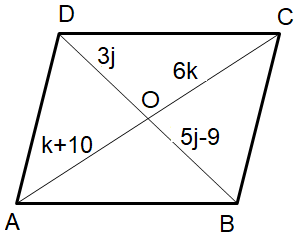
For the parallelogram given below, solve for j and k.
Problem 3 :
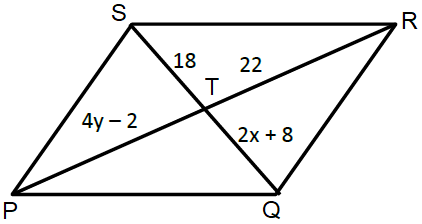
In parallelogram PQRS, solve for x and y.
Problem 4 :
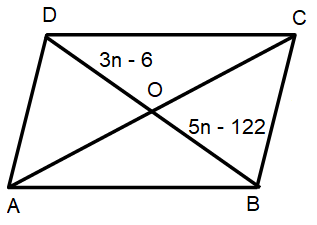
Solve the n in the following parallelogram ABCD. Find length of the diagonal BD.
Problem 5 :
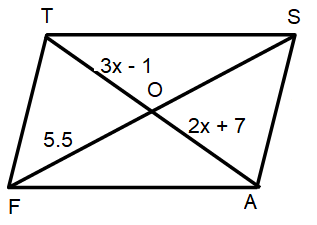
Length of the longer diagonal in the parallelogram FAST.
Problem 6 :
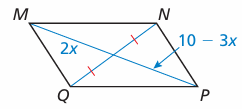
For what value of x is quadrilateral MNPQ a parallelogram? Explain your reasoning
Problem 7 :
find the value of x that makes the quadrilateral a parallelogram.
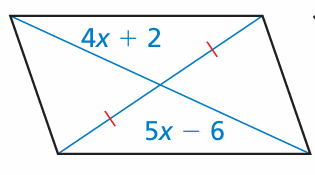
Problem 8 :
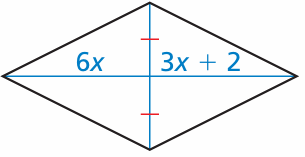
Problem 9 :
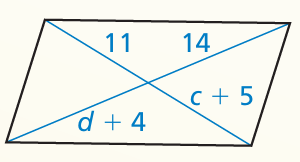
What value of x makes the quadrilateral a parallelogram? Explain how you found your answer.
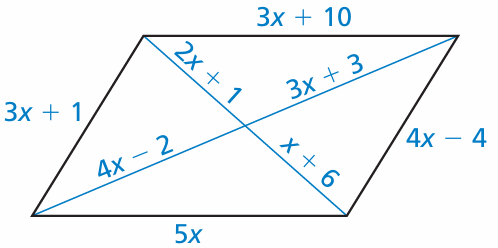
Problem 10 :
Find the value of each variable in the parallelogram.
Problem 11 :
Find the coordinates of the intersection of the diagonals of ▱QRST with vertices Q(−8, 1), R(2, 1), S(4, −3), and T(−6, −3).
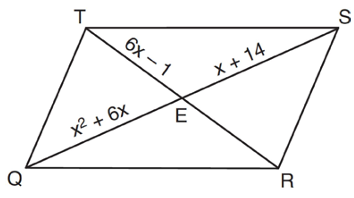
Problem 12 :
As shown in the diagram below, the diagonals of parallelogram QRST intersect at E. If QE = x2 + 6x, SE = x + 14, and TE = 6x − 1, determine TE algebraically
Answer Key
1) m = 4, n = 5
2) k = 2 and j = 4.5
3) x = 5 and y = 6
4) n = 58, length of the diagonal BD is 336.
5) length of the longer diagonal is 46.
6) the value of x is 2.
7) the value of x is 8
8) the value of x is 2/3.
9) x = 5
10) c = 6 and d = 10
11) (-2, -1)
12) the length TE is 11.
Problem 1 :
From the parallelogram given below, find the value of x, y and z.
Problem 2 :
If one angle of a parallelogram is 24 degree less than twice the smallest angle then, find the largest angle of the parallelogram.
Problem 3 :
In a parallelogram PQRS, if
∠P = (3x − 5)° and ∠Q = (2x + 15)°
then find the value of x.
Problem 4 :
If PQRS is a parallelogram, then ∠P − ∠R is
(a) 90° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 0°
Problem 5 :
Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are 3x - 4 and 3x + 10. Find the angles of parallelogram.
Problem 6 :
One angle of a parallelogram is 60 degree. Find its opposite angle and the adjacent angle.
Problem 7 :
Find the indicated measure in parallelogram MNOP, explain your reasoning.
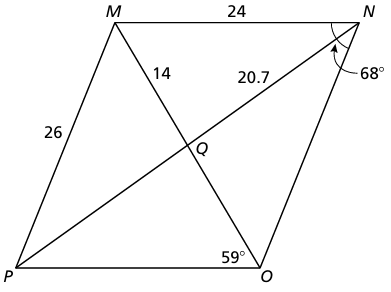
|
a) PO b) QO c) NO d) PQ |
e) m∠PMN f) m∠NOP g) m∠OPM h) m∠NMO |
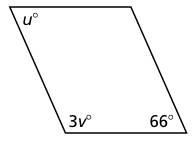
Problem 8 :
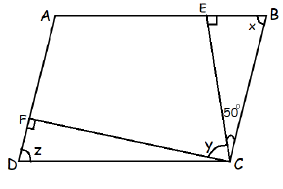
Problem 9 :
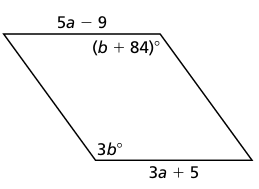
Problem 10 :
Find the value(s) of the variable(s) in each parallelogram
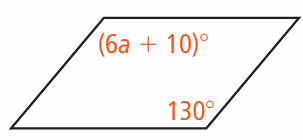
Problem 11 :
Two consecutive angles in a parallelogram have measures x + 5 and 4x - 10. Find the measure of the smaller angle.
Answer Key
1) x = 40, y = 40 and z = 40
2) the largest angle measure is 112.
3) x = 34
4) ∠P − ∠R = 0
5) the angles are 83 and 97.
6) In parallelogram, opposite angle will be equal. Opposite angle 60 degree is also 60 degree.
7) a) PO = 24 units
b) OQ = 14 units
c) NO = 26 units
d) PQ = 20.7 units
e) m∠PMN = 112
f) m∠NOM = 53
g) m∠OPM = 68
h) m∠NMO = 59 (Alternate interior angles are equal)
8) u = 66 and v = 38
9) a = 7 and b = 41
10) the value of a is 20.
11) the smaller angle measure is 32 degree.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling