RATIONAL FUNCTIONS AND ASYMPTOTES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Asymptotes are lines that the curve approaches at the edges of the coordinate plane.
Types of asymptotes :
Horizontal Asymptotes :
A horizontal asymptote is a horizontal line that is not part of a graph of a function but guides it for x – values “far” to the right and/or “far” to the left. The graph may cross it but eventually, for large enough or small enough values of x (approaching ±∞), the graph would get closer and closer to the asymptote without touching it.
A horizontal asymptote is a special case of a slant asymptote.
Let
deg N(x) = the degree of a numerator
and
deg D(x) = the degree of a denominator
Case 1 :
Degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
Case 2 :
Degree of numerator < degree of denominator
y = 0, which is the x – axis.
Case 3 :
degree of numerator > degree of denominator
There is no horizontal asymptote.
Vertical Asymptotes :
The Vertical Asymptotes of a rational function are found using the zeros of the denominator.
Oblique or slant asymptote :
A slant (oblique) asymptote occurs when the polynomial in the numerator is a higher degree than the polynomial in the denominator.
To find the slant asymptote you must divide the numerator by the denominator using either long division or synthetic division.
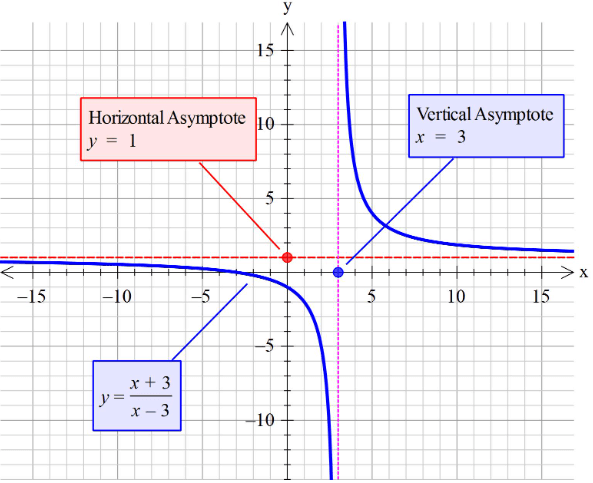
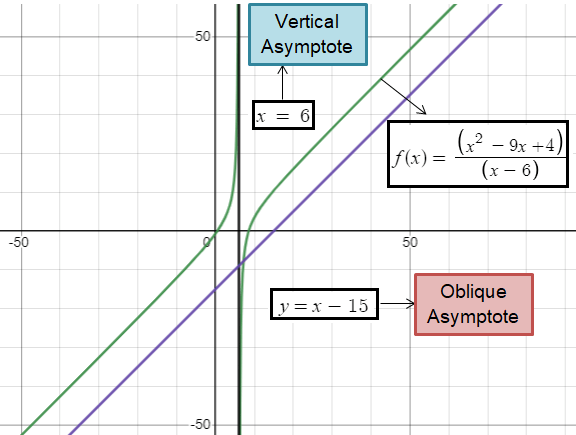
Find the horizontal asymptote of the graph of each rational function.
Problem 1 :
y = 2/(x – 6)
Solution :
y = 2/(x – 6)
Degree of numerator = 0
Degree of denominator = 1
degree of numerator < degree of denominator
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 which is the x – axis.
Problem 2 :
y = (x + 2)/(x – 4)
Solution :
y = (x + 2)/(x – 4)
Degree of numerator = 1
Degree of denominator = 1
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 1.
More problems on horizontal asymptotes
Describe the vertical asymptotes and holes for the graph of each rational function.
Problem 3 :
y = (x - 2)/(x + 2) (x - 2)
Solution :
y = (x - 2)/(x + 2) (x - 2)
We see x – 2 as a common factor in both numerator and denominator.
After cancel x – 2. We get,
1/(x + 2)
To find vertical asymptote, we equate the denominator to 0.
x + 2 = 0
x = -2
We see the hole at x = 2 in the graph.
x – 2 = 0 we will get hole at x = 2.
So, the vertical asymptote at x = -2; hole at x = 2.
More problems on vertical asymptotes
Find the oblique asymptote of the rational function
Problem 4 :
f(x) = (x2 + 8x – 20)/(x – 1)
Solution :
f(x) = (x2 + 8x – 20)/(x – 1)
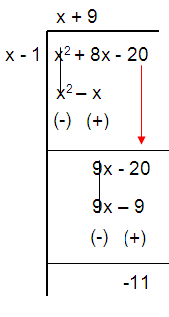
y = (x + 9) -11/(x – 1)
So, the oblique asymptote of the rational function is
y = x + 9
More problems on oblique asymptotes
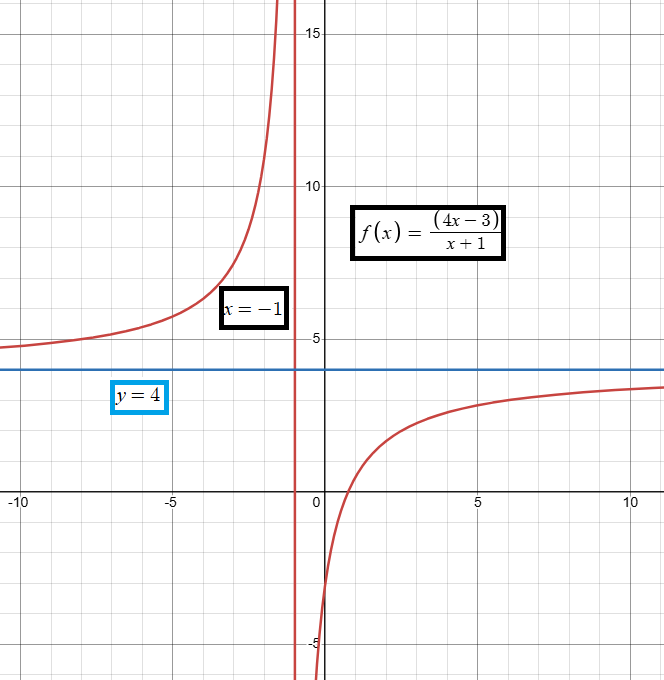
Problem 5 :
Consider the function f(x) = (4x - 3) / (x + 1)
a) State the equation of the vertical asymptote.
b) Use a table of values to determine the behaviour(s) of the function near its vertical asymptote.
c) State the equation of the horizontal asymptote.
d) Use a table of values to determine the end behaviors of the function near its horizontal asymptote.
e) Determine the domain and range.
f ) Determine the positive and negative intervals.
g) Sketch the graph
Solution :
f(x) = (4x - 3) / (x + 1)
a) The vertical asymptote is at x = -1
b) The intervals are (-∞, -1) and (-1, ∞)
- When x ∈ (-∞, -1), f(x) will be positive. That is, when x < -1, f(x) is positive
|
x - intercept : Put y = 0 4x - 3 = 0 x = 3/4 |
y - intercept : Put x = 0 f(0) = -3/1 y = -3 |
- When x ∈ (-1, 3/4), f (x) will be negative, when -1 < x < 3/4, f(x) is negative
- When x ∈ (3/4,∞), f(x) will be positive. That is, when x > 3/4, f(x) is positive.
y-intercept is -3/2.
c) Highest exponent of the numerator = 1, highest exponent of the denominator = 1
Equation of horizontal asymptote is y = 4/1
y = 4
d) End behavior :
- x --> -∞ then f(x) --> 4
- x --> ∞ then f(x) --> 4
e) Domain is all real numbers except x = -1
Range is all real values except y = 4
f)
- x ∈ (-∞, -1), f(x) will be positive.
- x ∈ (-1, 3/4), f (x) will be negative
- x ∈ (3/4,∞), f(x) will be positive
Problem 6 :
Read each set of conditions. State the equation of a rational function of the form
f(x) = (ax + b) / (cx + d)
that meets these conditions and sketch the graph.
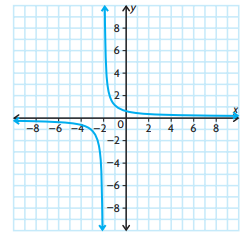
- Vertical asymptote at x = -2, horizontal asymptote at y = 0
- negative when x ∈ (-∞, -2), positive when x ∈ (-2, ∞) always decreasing.
Solution :
Since the vertical asymptote is x = -2, then (x + 2) is the denominator. Horizontal asymptote is y = 0 then highest exponent of the numerator should be lesser than the highest exponent of the denominator.
So, the required function may be
f(x) = 1/(x + 2)
Some more functions also can be created.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling