EQUATION OF HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Horizontal Asymptotes :
A horizontal asymptote is a horizontal line that is not part of a graph of a function but guides it for x – values “far” to the right and/or “far” to the left. The graph may cross it but eventually, for large enough or small enough values of x (approaching ±∞), the graph would get closer and closer to the asymptote without touching it.
A horizontal asymptote is a special case of a slant asymptote.
Let
deg N(x) = the degree of a numerator
and
deg D(x) = the degree of a denominator
Case 1 :
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
Case 2 :
degree of numerator < degree of denominator
y = 0 which is the x – axis.
Case 3 :
degree of numerator > degree of denominator
There is no horizontal asymptote.
Find the horizontal asymptote of the graph of each rational function.
Problem 1 :
y = 2/(x – 6)
Solution :
y = 2/(x – 6)
Degree of numerator = 0
Degree of denominator = 1
degree of numerator < degree of denominator
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 which is the x – axis.
Problem 2 :
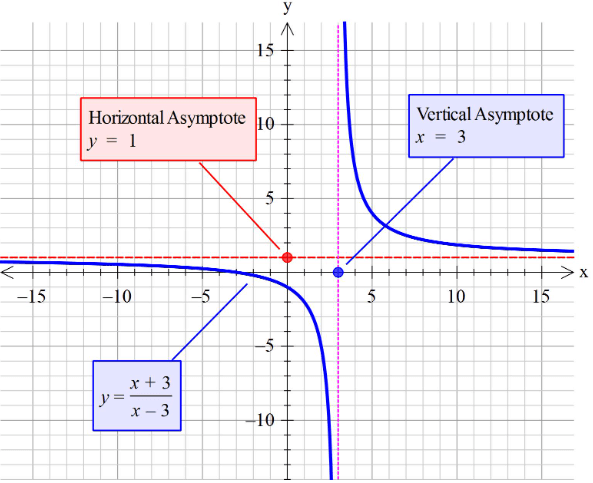
y = (x + 2)/(x – 4)
Solution :
y = (x + 2)/(x – 4)
Degree of numerator = 1
Degree of denominator = 1
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 1.
Problem 3 :
y = (x + 3)/2(x + 4)
Solution :
Given, y = (x + 3)/2(x + 4)
Degree of numerator = 1
Degree of denominator = 1
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 1/2.
Problem 4 :
y = (2x2 + 3)/(x2 – 6)
Solution :
y = (2x2 + 3)/(x2 – 6)
Degree of numerator = 2
Degree of denominator = 2
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 2.
Problem 5 :
y = (3x - 12)/(x2 – 2)
Solution :
Given, y = (3x - 12)/(x2 – 2)
Degree of numerator = 0
Degree of denominator = 2
degree of numerator < degree of denominator
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 which is the x – axis.
Problem 6 :
y = (3x3 – 4x + 2)/(2x3 + 3)
Solution :
y = (3x3 – 4x + 2)/(2x3 + 3)
Degree of numerator = 3
Degree of denominator = 3
degree of numerator = degree of denominator
y = leading coefficient of N(x)/leading coefficient of D(x).
y = 3/2
So, equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 1.5.
For each function, determine the equations of any vertical asymptotes, the locations of any holes, and the existence of any horizontal or oblique asymptotes.
Problem 7 :
y = x/(x + 4)
Solution :
y = x/(x + 4)
Highest exponent of the numerator = 1, highest exponent of the denominator = 1
Equation of horizontal asymptote = 1/1
Then y = 1 is the horizontal asymptote.
Equation of vertical asymptote is at x = -4.
Since there is no common factor in the numerator and in the denominator, there is no hole.
Problem 8 :
y = 1/(x - 5) (x + 3)
Solution :
y = 1/(x - 5) (x + 3)
There is no hole. Vertical asymptotes are at x = 5 and x = -3.
Highest exponent of the numerator = 0
highest exponent of the denominator = 2
N < D
So, x-axis or y = 0 is the horizontal asymptote.
Problem 9 :
y = (x + 4) / (x2 - 16)
Solution :
y = (x + 4) / (x2 - 16)
Factoring the denominator, we get
y = (x + 4) / (x + 4)(x - 4)
Common factor is x + 4, then there is a hole at x = -4.
Vertical asymptote is at x = 4
Highest exponent of the numerator = 1
Highest exponent of the denominator = 2
Equation of horizontal asymptote y = 1/1
y = 1
Problem 10 :
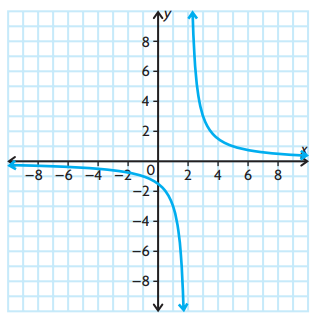
Consider the function
f(x) = 3/(x - 2)
a) State the equation of the vertical asymptote.
b) Use a table of values to determine the behaviour(s) of the function near its vertical asymptote.
c) State the equation of the horizontal asymptote.
d) Use a table of values to determine the end behaviours of the function near its horizontal asymptote.
e) Determine the domain and range.
f ) Determine the positive and negative intervals.
g) Sketch the graph.
Solution :
f(x) = 3/(x - 2)
a) The vertical asymptote is at x = 2
b) The intervals are (-∞, 2) and (2, ∞)
- When x ∈ (-∞, 2), f(x) will be negative. That is, when x < 2, f(x) is negative.
- When x ∈ (2, ∞), f(x) will be positive. That is, when x > 2, f(x) is positive.
y-intercept is -3/2.
c) Highest exponent of the numerator = 0, highest exponent of the denominator = 1
Equation of horizontal asymptote is x-axis or y = 0.
d) End behavior :
- x --> -∞ then f(x) --> 0
- x --> ∞ then f(x) --> 0
e) Domain is all real numbers except x = 2
Range is all real values except y = 0
f)
- x ∈ (-∞, 2), f(x) will be negative
- x ∈ (2, ∞), f(x) will be positive
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling