FINDING THE POINT OF DISCONTINUITY WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Find any points of discontinuity for each rational function.
Problem 1 :
y = (x + 3)/(x – 4) (x + 3)
Problem 2 :
y = (x - 2)/(x2 – 4)
Problem 3 :
y = (x - 3) (x + 1)/(x – 2)
Problem 4 :
y = 3x(x + 2)/x(x + 2)
Problem 5 :
y = 2/(x + 1)
Problem 6 :
y = 4x/(x3 – 9x)
Problem 7 :
Check the function
g(x) = (x2 + 7x + 10)/(x - 3)(x + 2)
for discontinuities. Conduct appropriate tests to determine if asymptotes exist at the discontinuity values. State the equations of any asymptotes and the domain of g(x)
Problem 8 :
Match the equation of each rational function with the most appropriate graph. Explain your reasoning.
a) y = (x + 4) / (x2 - 3x - 4)
b) y = (x + 4) / (x2 + 5x + 4)
c) y = (x2 + 4x)/(x + 4)
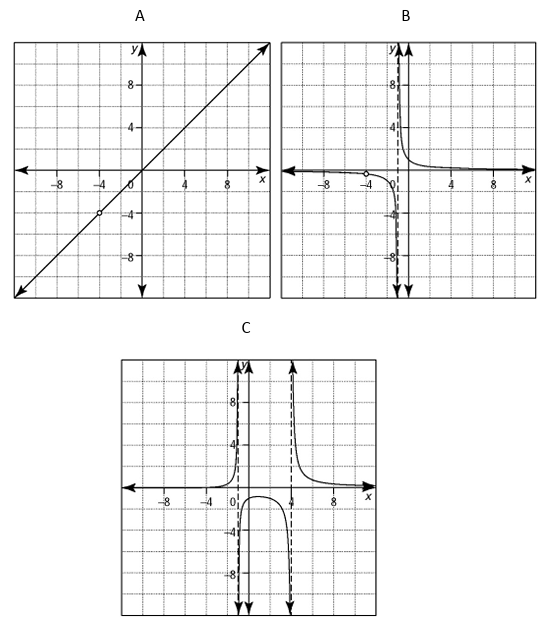
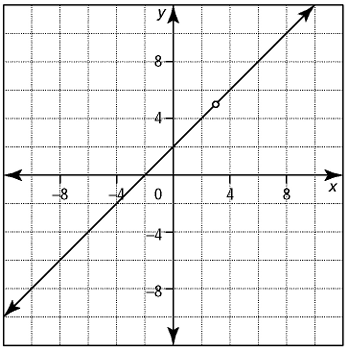
Problem 9 :
Write the equation for each graphed rational function
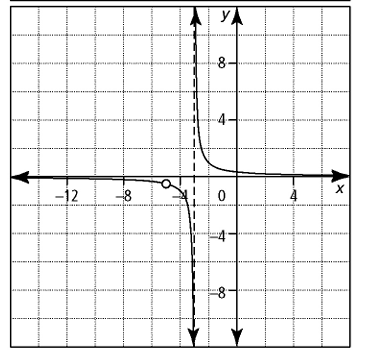
Problem 10 :
Write the equation for each graphed rational function.
Answer Key
1) x = -3 and 4
2) x = ±2
3) x = 2
4) x = 0, -2
5) x = -1
6) x = 0, ±3
7) Domain is all real values except -2 and 3.
8) a) Option c
b) Option b
c) Option a
9) y = (x + 2)(x - 3)/(x - 3)
10) y = (x + 5)/(x + 5)(x + 3)
Find the points of discontinuity. Classify each point as a vertical asymptote or a hole.
Problem 1 :
y = x/(x2 – 9)
Problem 2 :
y = (3x2 – 1)/x3
Problem 3 :
y = (6x2 + 3)/(x – 1)
Problem 4 :
y = (5x3 – 4)/(x2 + 4x – 5)
Problem 5 :
y = 7x/(x3 + 1)
Problem 6 :
y = (12x4 + 10x – 3)/3x4
Problem 7 :
y = (12x + 24)/(x2 + 2x)
Problem 8 :
y = (x2 – 1)/(x2 + 3x + 2)
Problem 9 :
y = (x2 – 1)/(x2 - 2x - 3)
Answer Key
1) Vertical asymptotes are at x = 3 and -3, no hole
2) Vertical asymptotes is at x = 0.No hole
3) Vertical asymptote is at x = 1.No hole
4) Vertical asymptotes are at x = -5 and 1.No hole
5) Asymptote at x = -1.No hole
6) Asymptote at x = 0. No hole
7) At x = 0, we have vertical asymptote, hole is at x = -2
8) vertical asymptote is at x = -2, hole is at x = -1.
9) Vertical asymptote is at x = 3, hole is at x = -1
State whether or not each of the following functions is continuous.
- If not, state where the discontinuity occurs and whether or not it is removable.
- Is the discontinuity is an asymptote, a hole or jump ?
- If an asymptote, what is its equation ?
Problem 1 :
f(x) = x/(x2 + 1)
Problem 2 :
f(x) = x/(2x2 - x - 1)
Problem 3 :
f(x) = (2x + 3)/(x2 - x - 6)
Problem 4 :
f(x) = (x - 4)/(x2 - 16)
Problem 5 :
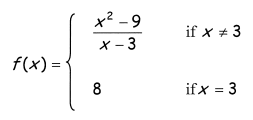
Problem 6 :
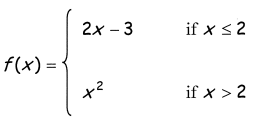
Problem 7 :
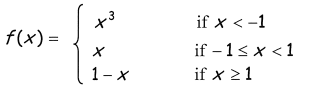
Problem 8 :
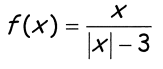
Problem 9 :
Find the value of a if the function is continuous.
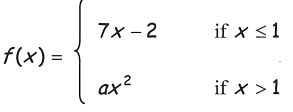
Problem 10 :
Find the value of a if the function is continuous.
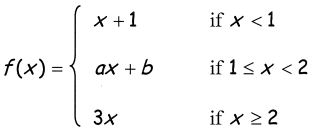
Problem 12 :
The graph of the function 𝑓(𝑥) is shown below :
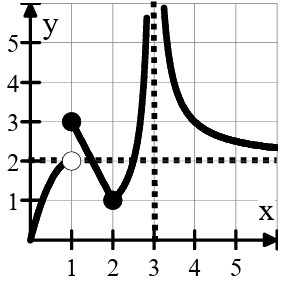
Which of the following statements is true about 𝑓?
I. 𝑓 is undefined at 𝑥 = 1.
II. 𝑓 is defined but not continuous at 𝑥 = 2.
III. 𝑓 is defined and continuous at 𝑥 = 3.
(A) Only I (B) Only II (C) I and II (D) I and III
(E) None of the statements are true.
Answer Key
1)
The function is discontinuous at x = -1/2 and 1.
Type of discontinuity = Non removable
Vertical asymptotes are at x = -1/2 and x = 1.
2)
The function is discontinuous at x = -1/2 and 1.
Type of discontinuity = Non removable
Vertical asymptotes are at x = -1/2 and x = 1.
3)
The function is discontinuous at x = 3 and -2.
Type of discontinuity = Non removable
Vertical asymptotes are at x = 3 and x = -2.
4)
So, the vertical asymptote is at x = -4
Hole is at x = 4. When x = 4, y = 1/5
5) The function is not continuous at x = 3, there is removable discontinuity at (3, 6).
6) Since Lim x->2- f(x) = Lim x->2+ f(x), then lim x ->2 f(x) does not exists.
Type of discontinuity = Jump discontinuity
7)
At x = 1, the function is not continuous, then the limit does not exists.
There is jump discontinuity at x = 1.
8) f(x) is not continuous at x = 3 and x = -3, there is vertical asymptote at x = 3 and x = -3
9) a = 5
10) a = 4/3
11) a = 4 and b = -2
12) Option C
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling