USING RATES OF CHANGE TO CREATE A GRAPHICAL MODEL
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Displacement versus time graph :
On a displacement (distance, height, or depth) versus time graph, the magnitude of the slope of a secant line represents the average speed on the corresponding interval. The magnitude of the slope of a tangent line represents the instantaneous speed at a specific point. As a result, observing how the slopes of tangent lines change at different points on a graph gives you insight into how the speed changes over time.
Problem 1 :
Today Steve walked to his part-time job. As he started walking, he sped up for 3 min. Then he walked at a constant pace for another 2 min. When he realized that he would be early for work, he slowed down. His walk ended and he came to a complete stop once he reached his destination 10 min after he started.
Solution :
Create a speed versus time graph for Steve’s walk to work.
Part 1 :
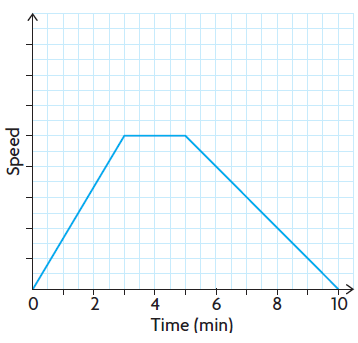
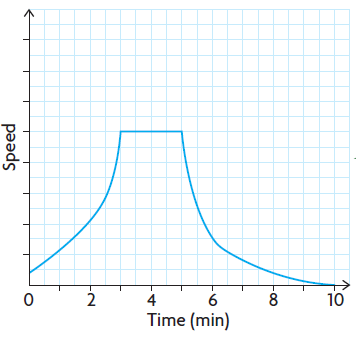
Starting from the initial position and speeding up for 3 minutes. It is clear that when time increases the speed will also increase. From 0 minutes to 3 minutes, we may draw two different curves to show the changes occurring with constant speed or variable speed.
Part 2 :
He is walking at the same speed for 2 minutes, so from 3 minutes to 5 times, he is walking at the constant speed. Drawing the horizontal line will show there is no change in speed.
Part 3 :
He is slowing down and reaches the destination after 10 minutes. So, from 5 to 10 minutes his speed is reducing we might draw the falling line to represent it is slowing down.
Assuming he walked at the constant speed :
Assuming he walked at the variable speed :
Problem 2 :
A cyclist is observed moving at a speed of 10 m/s. She begins to slow down at a constant rate and, 4 s later, is at a speed of 5 m/s. She continues to slow down at
a different constant rate and finally comes to a stop 6 s later.
a) Sketch a graph of speed versus time.
b) What is the average rate of change of the cyclist’s speed in the first 4 s?
c) Estimate the instantaneous rate of change in speed at 3 s.
Solution :
a)
Horizontal axis - time
Vertical axis - speed
Step 1 :
Slowing down, so we draw the falling curve to show this. The starting position of the graph must be (0, 10).
Step 2 :
After 4 seconds his speed is 5 meter per second, then plot the point (4, 5)
Step 3 :
From the point (4, 5) also we have to draw the falling curve to show it continues to slow down and ending point must be (6, 0).
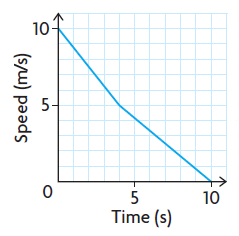
b) Average rate of change = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
(0, 10) and (4, 5)
= (5 - 10) / (4 - 0)
= -5/4
= -1.25 m/s2
c) To find instantaneous rate of change, we have to select points near by 3 seconds and then approximate.
Equation of the linear function representing the first part :
y = mx + b
y = (-5/4)x + 10
When x = 3.1, y = 6.125
When x = 2.9, y = 6.375
Instantaneous rate of change = (6.375 - 6.125) / (2.9 - 3.1)
= 0.25/(-0.2)
= -1.25 m/s2
Problem 3 :
A flask, a beaker, and a graduated cylinder are being filled with water. The rate at which the water flows from the tap is the same when filling all three containers. Draw possible water level versus time graphs for the three containers.

Solution :
A flask :
Since the diameter of the flask varies, so increase in water level will be slow comparing the time. So, the curve representing the situation cannot be linear.
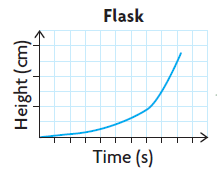
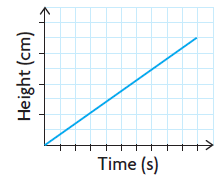
Graduated Cylinder :
Water will increase constantly faster comparing the rate in beaker. So, the curve must be a straight line.
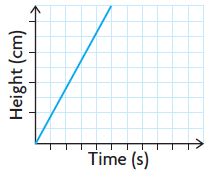
Beaker :
Water will increase constantly but comparing the cylinder it is slower. So, the curve representing the rate of change must be straight line has the lesser slope.
Problem 4 :
The following graphs show distance versus time. Match each graph with the description given below
a)
A) Distance is decreasing
B) There is no change in distance over the time
C) Distance is increasing
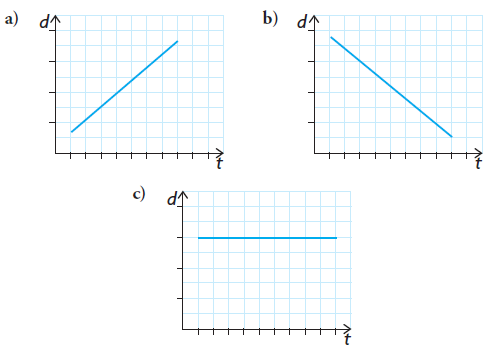
b) Which of the graphs show that the speed is constant? Explain
Solution :
x-axis ==> Time
y - axis ==> Distance
A) Distance is decreasing :
Graph b represents the falling line and it shows the distance is decreasing when time increases.
B) There is no change in distance over the time :
Graph c represents the graph of horizontal line, there is no change in distance.
C) Distance is increasing
Graph a represents the falling line and it shows the distance is increasing when time decreases.
Problem 5 :
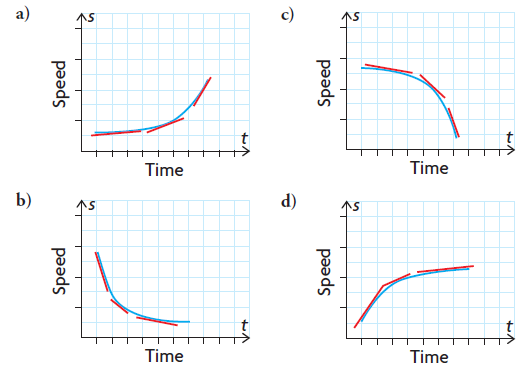
The following graphs show speed versus time. Match each graph with the description given below.
A) The rate at which the speed increases is increasing as time decreases.
B) The rate at which the speed increases is decreasing as time increases.
C) The rate at which the speed decreases is decreasing as time increases.
D) The rate at which the speed decreases is increasing as time increases.
Solution :
A) The rate at which the speed increases is increasing as time decreases.
Graph a
B) The rate at which the speed increases is decreasing as time increases.
Graph c
C) The rate at which the speed decreases is decreasing as time increases.
Graph d
D) The rate at which the speed decreases is increasing as time increases.
Graph b
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling