USE FIRST DERIVATIVE TEST TO FIND EXTREMA
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To find extrema using the first derivative test, we have to use the steps given below.
- Let f(x) be the defined function on (a, b).
- Find the first derivative of the function. That is f'(x).
- Set f'(x) = 0, and find the critical numbers.
- Plot those critical numbers in the number line and divide into intervals.
Applying one of the values from the interval,
Based on the sign of f'(x), we can decide the function is increasing or decreasing on the interval.
- If the sign of f'(x) changes from negative to positive, we can say there is relative minimum.
- If the sign of f'(x) changes from positive to negative, we can say there is relative maximum.
Find the following :
(a) find the critical numbers of f, if any,
(b) find the open intervals on which the function is increasing or decreasing,
(c) apply the First Derivative Test to identify all relative extrema, and
(d) use a graphing utility to confirm your results.
Problem 1 :
f(x) = x2 − 8x
Solution :
f(x) = x2 − 8x
f'(x) = 2x - 8
f'(x) = 2(x - 4)
f'(x) = 0
2(x - 4) = 0
x = 4
Critical number is at x = 4
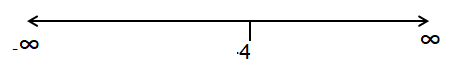
Intervals are (-∞, 4) and (4, ∞)
|
-∞ < x < 4 |
x = -5 ∈ (-∞, 4) |
f'(-5) = 2(-5 - 4) f'(-5) = -18 < 0 |
|
4 < x < ∞ |
x = 5 ∈ (4, ∞) |
f'(5) = 2(5 - 4) f'(5) = 2 > 0 |
- In the interval (-∞, 4), we have negative slope. So, it is decreasing in the interval (-∞, 4).
- In the interval (4, ∞), we have positive slope. So, it is increasing in the interval (4, ∞).
Negative --> Positive --> Relative minimum
Relative minimum at x = 4
f(4) = 42 − 8(4)
f(4) = 16 − 32
f(4) = -16
Relative minimum is (4, -16)
Problem 2 :
f(x) = -2x2 + 4x + 3
Solution :
f(x) = -2x2 + 4x + 3
f'(x) = -4x + 4
f'(x) = -4(x - 1)
f'(x) = 0
-4(x - 1) = 0
x = 1
Critical number is at x = 1

Intervals are (-∞, 1) and (1, ∞)
|
-∞ < x < 1 |
x = 0 ∈ (-∞, 1) |
f'(x) = -4(x - 1) f'(0) = -4(0 - 1) f'(0) = 4 > 0 |
|
1 < x < ∞ |
x = 2 ∈ (1, ∞) |
f'(2) = -4(2 - 1) f'(2) = -4 < 0 |
- In the interval (-∞, 1), we have positive slope. So, it is increasing in the interval (-∞, 1).
- In the interval (1, ∞), we have negative slope. So, it is decreasing in the interval (1, ∞).
Positive --> Negative --> Relative maximum
Relative maximum x = 1
f(1) = -2(1)2 + 4(1) + 3
f(1) = -2 + 4 + 3
f(1) = -2 + 7
f(1) = 5
Relative maximum is (1, 5)
Problem 3 :
f(x) = -7x3 + 21x + 3
Solution :
f(x) = -7x3 + 21x + 3
f'(x) = -21x2 + 21
f'(x) = -21(x2 - 1)
f'(x) = 0
-21(x2 - 1) = 0
x2 - 1 = 0
x = ±1
Critical number is at x = -1 and 1
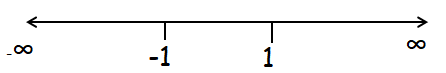
Intervals are (-∞, -1), (-1, 1) and (1, ∞)
|
-∞ < x < -1 |
x = -2 ∈ (-∞, -1) |
f'(x) = -21(x2 - 1) f'(-2) = -21(4 - 1) f'(-2) = -63 < 0 |
|
-1 < x < 1 |
x = 0 ∈ (-1, 1) |
f'(0) = -21(x2 - 1) f'(-2) = -21(-1) f'(-2) = 21 > 0 |
|
1 < x < ∞ |
x = 2 ∈ (1, ∞) |
f'(2) = -21(x2 - 1) f'(2) = -21(3) f'(-2) = -63 < 0 |
- In the interval (-∞, -1), we have negative slope. So, it is decreasing in the interval (-∞, -1).
- In the interval (-1, 1), we have positive slope. So, it is increasing in the interval (-1, 1).
- In the interval (1, ∞), we have negative slope. So, it is decreasing in the interval (1, ∞).
Negative --> Positive --> Relative minimum
Positive --> Negative --> Relative maximum
Relative minimum at x = -1
f(-1) = -7(-1)3 + 21(-1) + 3
f(-1) = -7 - 21 + 3
f(-1) = -28 + 7
f(-1) = -21
Relative minimum is (-1, -21)
Relative maximum at x = 1
f(1) = -7(1)3 + 21(1) + 3
f(1) = -7 + 21 + 3
f(1) = -7 + 24
f(1) = 17
Relative maximum is (1, 17)
Problem 4 :
f(x) = (x - 1)2(x + 3)
Solution :
f(x) = (x - 1)2(x + 3)
Using product rule, finding the derivative. we get
u = (x - 1)2 and v = (x + 3)
u' = 2(x - 1) and v' = 1
f'(x) = (x - 1)2(1) + 2(x - 1)(x + 3)
f'(x) = x2- 2x + 1 + 2(x2 + 2x - 3)
f'(x) = x2- 2x + 1 + 2x2 + 4x - 6
f'(x) = 3x2 + 2x - 5
f'(x) = 3x2 + 2x - 5 = 0
(3x + 5)(x - 1) = 0
x = -5/3 and x = 1
(-∞, -5/3), (-5/3, 1) and (1, ∞)
|
x = -2 ∈ (-∞, -5/3) |
f'(x) = (3x + 5)(3x - 2) f'(-2) = (-6 + 5)(-6 - 2) f'(-2) = 8 > 0 |
|
x = 0 ∈ (-5/3, 1) |
f'(x) = (3x + 5)(3x - 2) f'(0) = (5)(-2) f'(0) = -10 < 0 |
|
x = 2 ∈ (1, ∞) |
f'(x) = (3x + 5)(3x - 2) f'(2) = (11)(4) f'(2) = 44 > 0 |
- In the interval (-∞, -5/3), we have positive slope. So, it is increasing in the interval (-∞, -5/3).
- In the interval (-5/3, 1), we have negative slope. So, it is decreasing in the interval (-5/3, 1).
- In the interval (1, ∞), we have positive slope. So, it is increasing in the interval (1, ∞).
Positive --> Negative --> Relative maximum
Negative --> Positive --> Relative minimum
Relative maximum at x = -5/3
f(-5/3) = (-5/3 - 1)2(-5/3 + 3)
f(-5/3) = (64/9) (4/3)
f(-5/3) = 256/27
Relative minimum is (-5/3, 256/27)
Relative maximum at x = 1
f(1) = (1 - 1)2(1 + 3)
f(1) = 0
Relative minimum is (1, 0)
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling