UNION AND INTERSECTION OF SETS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
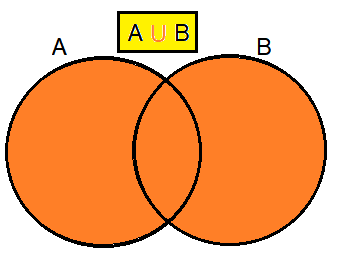
Union of two sets :
The union of two sets contains all the elements contained in either set (or both sets).
The union is notated A ⋃ B.
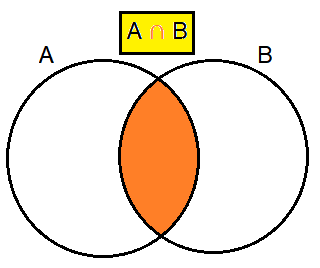
Intersection of two sets :
The intersection of two sets contains only the elements that are in both sets.
The intersection is notated A ⋂ B.
Problem 1 :
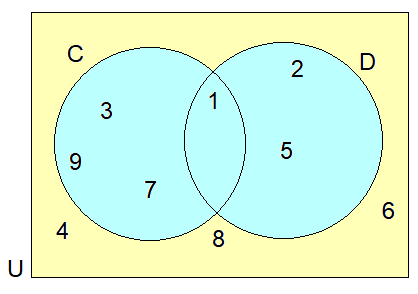
List :
|
i) Set C ii) Set D iii) Set U |
iv) Set C ∩ D v) Set C U D |
Solution :
i) Set C
The elements in set C = {1, 3, 7, 9}
ii) Set D
The elements in set D = {1, 2, 5}
iii) Set U
The universal set with all the elements in set
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
iv) Set C ∩ D
The common elements in set C and D is
C ∩ D = {1}
v) Set C U D
All the elements in sets C and D is
C U D = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9}
Problem 2 :
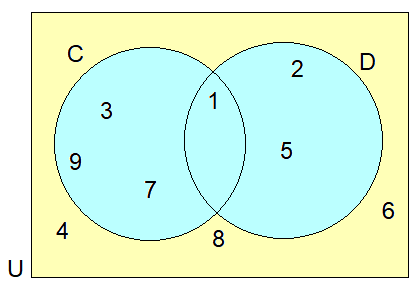
List :
|
(i) n(C) (ii) n(D) (iii) n(U) |
(iv) n(C ∩ D) (v) n(C U D) |
Solution :
(i) n(C)
The number of elements in set C is 4.
So, n(C) = 4
(ii) n(D)
The number of elements in set D is 3.
So, n(D) = 3
(iii) n(U)
The number of elements in universal set U is 9.
n(U) = 9
(iv) n(C ∩ D)
The number of common elements in sets C and D is 1.
n(C ∩ D) = 1
(v) n(C U D)
The number of all elements in sets C and D is 6.
n(C U D) = 6
Problem 3 :
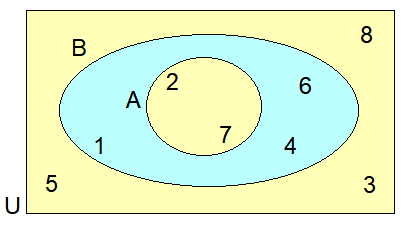
List :
|
(i) Set A (ii) Set B (iii) Set U |
(iv) Set A ∩ B (v) Set A U B |
Solution :
(i) A = {2, 7}
(ii) B = {1, 4, 6, 2, 7}
(iii) U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
(iv) A ∩ B = {2, 7}
(v) A U B = {1, 2, 4, 6, 7}
Problem 4 :
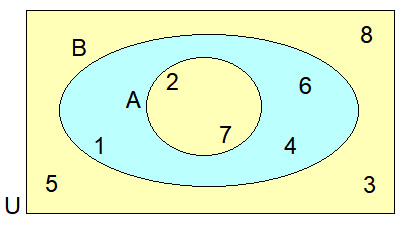
Find :
|
(i) n(A) (ii) n(B) (iii) n(U) |
(iv) n(A ∩ B) (v) n(A U B) |
Solution :
(i) n(A)
The number of elements in set A is 2.
So, n(A) = 2
(ii) n(B)
The number of elements in set B is 5.
So, n(B) = 5
(iii) n(U)
The number of elements in universal set U is 8.
n(U) = 8
(iv) n(A ∩ B)
The number of common elements in sets A and B is 2.
n(A ∩ B) = 2
(v) n(A U B)
The number of all elements in sets A and B is 5.
n(A U D) = 5
Problem 5 :
Consider U = {x│x ≤ 12, x € Z+},
A = {2, 7, 9, 10, 11} and B = {1, 2, 9, 11, 12}.
a) Show these sets on a Venn diagram.
b) List the elements of :
(i) A ∩ B
(ii) A U B
(iii) B’
c) Find :
|
(i) n(A) (ii) n(B’) |
(iii) n(A ∩ B) (iv) n(A U B) |
Solution :
a)
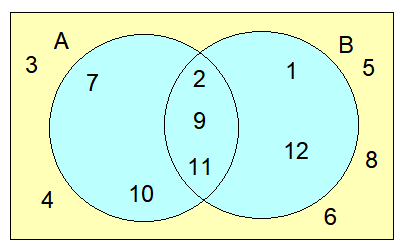
b)
(i) A ∩B = {2, 9, 11}
(ii) A U B = {1, 2, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12}
(iii) B’
The elements which do not belong to set B is
B’ = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10}
c)
(i) n(A) = 5
(ii) The number of elements which do not belong to set B is B’ = 7
(iii) n(A ∩ B) = 3
(iv) n(A U B) = 7
Problem 6 :
Of 30 students in student government, 20 are honor students and 9 are officers and honor students. All of the students are officers, honor students, or both. How many are officers but not honor students?
Solution :
Total number of students = 30
Let H be the number honor students and O be number of officers.
n(HnO) = 9
n(H) = 20
n(HUO) = n(H) + n(O) - n(HnO)
30 = 20 + n(O) - 9
30 = 11 + n(O)
n(O) = 30 - 11
n(O) = 19
Number of officers is 19.
Problem 7 :
In a class of 50 students each of the students passed either in math or in science or in both. 10 students passed in both and 28 passed in science. Find how many students passed in mathematics ?
Solution :
Let M and S be the number of students who passes in math and science.
n(M u S) = 50
n(M n S) = 10
n(S) = 28
n(MUS) = n(M) + n(S) - n(MnS)
50 = n(M) + 28 - 10
50 = n(M) + 18
n(M) = 50 - 18
n(M) = 32
Problem 8 :
A travel agent surveyed 100 people to find out how many of them had visited the cities of Melbourne and Brisbane. Thirty‑one people had visited Melbourne, 26 people had been to Brisbane, and 12 people had visited both cities.
Draw a Venn diagram to find the number of people who had visited:
a) Melbourne or Brisbane
b) Brisbane but not Melbourne
c) only one of the two cities
d) neither city
Solution :
Let M be the set of people who had visited Melbourne, and let B be the set of people who had visited Brisbane. Let the universal set E be the set of people surveyed.
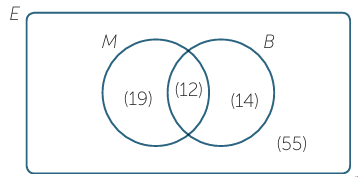
The information given in the question can now be rewritten as
n(M) = 31, n(B) = 26, n(M n B) = 12 and n(E) = 100.
Hence number in M only= 31 – 12 = 19
and
number in B only = 26 – 12 = 14.
a) Number visiting Melbourne or Brisbane = 19 + 14 +12 = 45.
b) Number visiting Brisbane only = 14.
c) Number visiting only one city = 19 + 14 = 33.
d) Number visiting neither city = 100 – 45 = 55.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling