MAXIMUM OR MINIMUM USING INSTANTANEOUS RATE OF CHANGE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
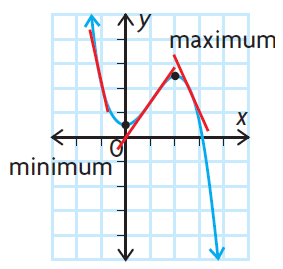
The instantaneous rate of change is zero at both a maximum point and a minimum point. As a result, the tangent lines drawn at these points will be horizontal lines
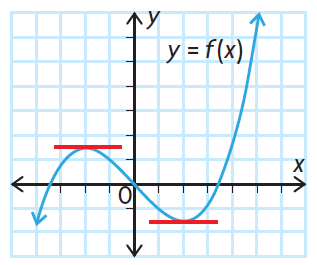
If the instantaneous rate of change is negative before the value where the rate of change is zero and positive after this value, then a minimum occurs. Graphically, the tangent lines must have a negative slope before the minimum point and a positive slope after.
If the instantaneous rate of change is positive before the value where the rate of change is zero and negative after this value, then a maximum occurs. Graphically, the tangent lines must have a positive slope before the maximum point and a negative slope after.
Problem 1 :
Leonard is riding a Ferris wheel. Leonard’s elevation h(t) in metres above the ground at time t in seconds, can be modelled by the function
h(t) = 5 cos (4(t - 10)°) + 6
Shu thinks that Leonard will be closest to the ground at 55 s. Do you agree? Support your answer.
Solution :
h(t) = 5 cos (4(t - 10)°) + 6
Using t = 54 and t = 55
Average rate of change = [h(55) - h(54)] / (55 - 54)
h(55) = 5 cos (4(55 - 10)°) + 6
= 5 cos (4(45))° + 6
= 5 cos 180° + 6
= 5(-1) + 6
= -5 + 6
= 1
h(54) = 5 cos (4(54 - 10)°) + 6
= 5 cos (4(44))° + 6
= 5 cos 176° + 6
= 5(-0.997) + 6
= -4.987 + 6
= 1.012
Average rate of change = (1 - 1.012)/1
= -0.012 meter/second
Using t = 55 and t = 56
Average rate of change = [h(56) - h(55)] / (56 - 55)
h(56) = 5 cos (4(56 - 10)°) + 6
= 5 cos (4(46))° + 6
= 5 cos 184° + 6
= 5(-0.997) + 6
= -4.987 + 6
= 1.012
Average rate of change = (1.012 - 1)/1
= 0.012 meter/second
Since the rate of change in height using a point to the left of t = 55 is negative and using the point to he right of t = 55 is positive and since it is close to 0, the instantaneous rate of change could be zero at t = 55. So, there could be minimum at t = 55.
Problem 2 :
Show that the minimum value of the function
f(x) = x2 + 4x - 21
happens when x = -2.
Solution :
f(x) = x2 + 4x - 21
Using difference quotient method,
= f(a + h) - f(a) / h
At x = -2
f(-2 + h) = (-2 + h)2 + 4(-2 + h) - 21
= (-2)2 + 2(-2)h + h2 + 4(-2) + 4h - 21
= 4 - 4h + h2 - 8 + 4h - 21
= h2 - 25
f(-2) = (-2)2 + 4(-2) - 21
= (-2)2 - 8 - 21
= 4 - 8 - 21
= 4 - 29
= -25
Applying these values in the formula, we get
= (h2 - 25 - (-25)) / h
= (h2 - 25 + 25) / h
= h
When h = -0.01
m = -0.01
When h = 0.01
m = 0.01
Average = (-0.01 + 0.01)/2
= 0
At x = -1.9
f(-1.9) = (-1.9)2 + 4(-1.9) - 21
= 3.61 - 7.6 - 21
= -24.99
At x = -2.1
f(-2.1) = (-2.1)2 + 4(-2.1) - 21
= 4.41 - 8.4 - 21
= 4.41 - 29.4
= -24.99
Sine the slope of the tangent is equal to 0 when x = -2 and since the values of the function when x = -2.1 and x = -1.9 are greater than the value when x = -2, a minimum value occurs at x = -2.
Problem 3 :
For each function, the point given is the maximum or minimum. Use the difference quotient to verify that the slope of the tangent at this point is zero.
f(x) = 0.5x2 + 6x + 7.5 at (-6, -10.5)
Solution :
f(x) = 0.5x2 + 6x + 7.5 at (-6, -10.5)
Using difference quotient method,
= f(a + h) - f(a) / h
at x = -6
f(-6 + h) = 0.5(-6 + h)2 + 6(-6 + h) + 7.5
= 0.5(36 - 12h + h2) - 36 + 6h + 7.5
= 18 - 6h + 0.5h2 - 36 + 6h + 7.5
= 0.5h2 - 18 + 7.5
= 0.5h2 - 10.5
f(-6) = 0.5(-6)2 + 6(-6) + 7.5
= 0.5(36) - 36 + 7.5
= 18 - 36 + 7.5
= -10.5
Applying these values in the formula, we get
= (0.5h2 - 10.5 - (-10.5)) / h
= (0.5h2 - 10.5 + 10.5) / h
= 0.5h2 / h
= 0.5h
When h = -0.01
= 0.5(-0.01)
m = -0.005
When h = 0.01
= 0.5(0.01)
m = 0.005
Average = (-0.005 + 0.005)/2
= 0
Since the instantaneous rate of change is 0 at x = -6, it has minimum at x = -6.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling