HOW TO FIND THE DERIVATIVE OF A INVERSE FUNCTION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The Derivative of an Inverse Function :
Let f be a differentiable function whose inverse function f-1 is also differentiable. Then providing that the denominator is not zero.
Problem 1 :
Let f(x) = x2 - (3/x)
a) What is the value of f-1(8) ?
b) What is the value of (f-1)' (8) ?
Solution :
In a function y and f(x) both are equal. That is,
y = f(x)
f-1(y) = x
a) Given that,
f(x) = x2 - (3/x)
In f-1(8), y = 8. Then f(x) = 8
8 = (x3 - 3)/x
8x = x3 - 3
x3 - 8x - 3 = 0
Solving using synthetic division, we get
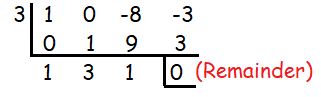
3 is a solution. So, the value of f-1(8) is 3.
b)
Problem 2 :
If f(2) = 5 and f'(2) = 1/4, find (f-1)' (5)
Solution :
(f-1)' (x) = 1/f' [(f-1) (x)]
Given that, f(2) = 5
f-1(5) = 2
Given that, f'(2) = 1/4
(f-1)' (1/4) = 2
(f-1)' (5) = 1/f' [(f-1) (5)]
Applying the value of (f-1) (5) = 2 in above, we get
= 1/f' (2)
Applying the value of f' (2) = 4 in above,
= 1/(1/4)
= 1 (4/1)
= 4
So, the answer is 4.
Problem 3 :
Let f and g be functions that are differentiable everywhere. If g is the inverse function of f and if g(3) = 4 and f'(4) = 3/2, then g'(3) ?
a) 1/4 b) 1/3 c) 2/3 d) 4/3
Solution :
Given that g(3) = 4,
Since g and f are inverse to each other.
f(g(x)) x
f'(g(x)) g'(x) = 1
f'(g(3)) g'(3) = 1
Applying the value of g(3), we get
f'(4) g'(3) = 1
g'(3) = 1/f'(4)
Applying the value of f'(4), we get
g'(3) = 1/(3/2)
= 1 x (2/3)
g'(3) = 2/3
So, the answer is option c.
Problem 4 :
If f(-3) = 2 and f'(-3) = 3/4, then (f-1)' (2) = ?
a) 1/2 b) 4/3 c) 3/2 d) -3/4
Solution :
Given that f(-3) = 2
f-1(2) = -3
(f-1)' (x) = 1/f' [(f-1) (x)]
(f-1)' (2) = 1//f' [(f-1) (2)]
Applying the value of (f-1) (2) = -3, we get
= 1/f' (-3)
Applying the value of f' (-3) = 3/4, we get
= 1/(3/4)
= 4/3
So, the answer is 4/3.
Problem 5 :
If f(x) = x3 - x + 2, then (f-1)'(2) = ?
Solution :
f(x) = x3 - x + 2
f'(x) = 3x2 - 1 + 0
f'(x) = 3x2 - 1
(f-1)'(2) = 1/f'( (f-1)(2) ) ----(1)
Finding the value of (f-1)(2) :
2 = x3 - x + 2
0 = x3 - x
x(x2 - 1) = 0
x = 0, x = 1 and -1.
So, the value of (f-1)(2) are 0, 1 and -1.
Applying these values one by one, we get
(f-1)'(2) = 1/f' (0 )
Evaluating f'(0) from f'(x) = 3x2 - 1 :
f'(0) = 3(0)2 - 1 ==> -1
Applying this value in (1), we get
= 1/(-1)
= -1
Evaluating f'(1) from f'(x) = 3x2 - 1 :
f'(1) = 3(1)2 - 1 ==> 2
Applying this value in (1), we get
= 1/2
Evaluating f'(-1) from f'(x) = 3x2 - 1 :
f'(-1) = 3(-1)2 - 1 ==> 2
Applying this value in (1), we get
= 1/2
Problem 6 :
If f(x) = sin x, then (f-1)' (√3/2) = ?
a) 1/2 b) 2√3/3 c) √3 d) 2
Solution :
(f-1)' (√3/2) = 1/f'( (f-1) (√3/2) ) ---(1)
f(x) = sin x
Finding (f-1) (√3/2) :
√3/2 = sin x
x = sin-1(√3/2)
x = π/3
(f-1) (√3/2) = π/3
Applying this value in (1), we get
(f-1)' (√3/2) = 1/f'(π/3)
from f(x) = sin x, f'(x) = cos x
f'(π/3) = cos (π/3)
(f-1)' (√3/2) = 1/2
So, the answer is 1/2.
Problem 7 :
If f(x) = 1+ ln x, then (f-1)' (2)
a) -1/e b) 1/e c) -e d) e
Solution :
If (x) = 1+ ln x
(f-1)' (2) = 1/f'((f-1) (2)) ----(1)
Finding (f-1) (2)) :
f (x) = 1 + ln x
2 = 1 + ln x
1 = ln x
x = e1
x = e
(f-1) (2)) = e
The value of (f-1) (2)) is e.
(f-1)' (2) = 1/f'(e)
From f(x) = 1 + ln x
f'(x) = 0 + 1/x
f'(x) = 1/x
f'(e) = 1/e
Then, (f-1)' (2) = 1/f'(e)
(f-1)' (2) = 1/(1/e)
= e
So, the answer is e.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling