HOW TO FIND THE ANGLES OF A PARALLELOGRAM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Definition of parallelogram :
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral which has opposite sides parallel.
Properties of parallelogram :
- Opposite angles are equal in size.
- Consecutive interior angles add upto 180.
- Vertical angles are a pair of non-adjacent angles formed by the intersection of two straight lines and are opposite to each other.
Find the measures of the indicated angles in each parallelogram.
Problem 1 :
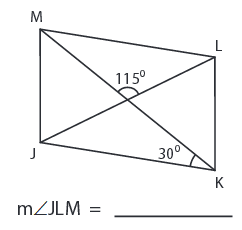
Solution :
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
∠KML = ∠MKJ = 30°
∠KML + ∠JLM + 115° = 180°
∠JLM + 30° + 115° = 180°
∠JLM = 180° - 115° - 30°
∠JLM = 35°
Problem 2 :
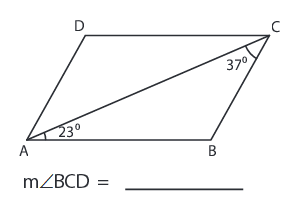
Solution :
DC II AB
∠DCA = ∠BAC = 23°
∠BCD = ∠ACB + ∠DCA
∠BCD = 23° + 37°
∠BCD = 60°
Problem 3 :
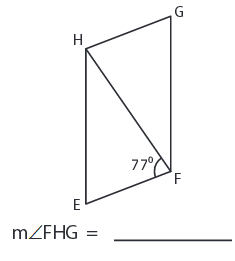
Solution :
The opposite angles are equal in a parallelogram.
∠FHG = ∠HFE = 77°
So, ∠FHG = 77°
Problem 4 :
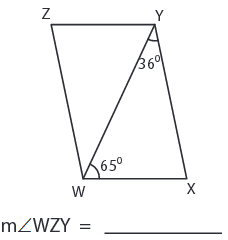
Solution :
The opposite angles are equal in a parallelogram.
∠WZY = ∠WXY
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
∠WXY = 180° - ∠XWY - ∠WYX
∠WZY = = 180° - 65° - 36°
∠WZY = = 79°
∠WZY = 79°
Problem 5:
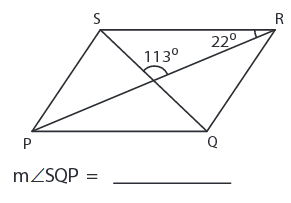
Solution :
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
∠SQP = 180° - (113 + 22)
∠SQP = 180° - 135°
∠SQP = 45°
Problem 6:
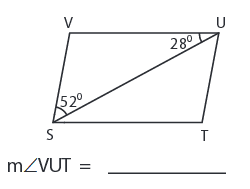
Solution :
∠VUT = ∠SUV + ∠SUT
∠VUT = 28° + 52°
∠VUT = 80°
Problem 6 :
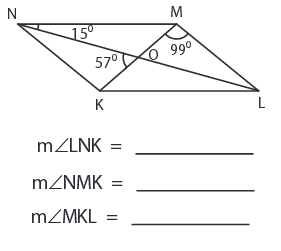
Solution :
In MNKL, ML II NK
So, ∠LNK = ∠NLM
∠MOL = ∠KON = 57° (vertical angles are equal)
∠LNK = 180° - ∠OML - ∠MOL
∠LNK = 180° - 99° - 57°
∠LNK = 24°
In ∆OMN,
∠NOK = ∠LNM + ∠OMN
∠OMN = ∠NOK - ∠LNM
∠OMN = 57° - 15°
∠OMN = 42°
The outside angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two interior angles that are not adjacent to it.
NM II KL,
So, ∠MKL = ∠NMK = 42°
Problem 7 :
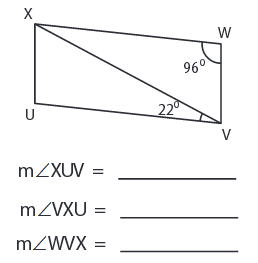
Solution :
∠XUV = ∠XWV = 96°
∠VXU = 180° - ∠XWV - ∠XVU
∠VXU = 180° - 96° - 22°
∠VXU = 62°
∠WVX = ∠VXU = 62°
Problem 8 :
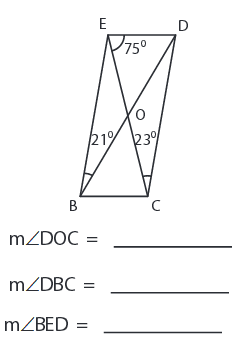
Solution :
BE II DC,
∠EBD = ∠BDC = 21°
∠DOC = 180° - (∠BDC + ∠DCE)
∠DOC = 180° - (21 + 23)
∠DOC = 180° - 44°
∠DOC = 136°
ED II BC,
∠DEC = ∠ECB = 75°
∠DBC = ∠DOC - ∠ECB
∠DBC = 136° - 75°
∠DBC = 61°
∠ECD = ∠BEC = 23°
∠BED = ∠BEC + ∠DEC
∠BED = 23° + 75°
∠BED = 98°
Find the measures of the numbered angles for each parallelogram.
Problem 9 :
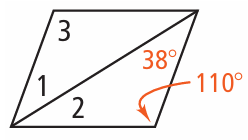
Solution :
Opposite angels will be equal.
∠3 = 110
Adjacent angles are co-interior angles.
∠1 + ∠2 = 180 - 110
∠1 + ∠2 = 70
∠1 = 38
38 + ∠2 = 70
∠2 = 70 - 38
∠2 = 32
Problem 10 :
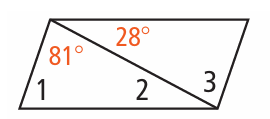
Solution :
∠2 = 28
∠3 = 81
∠1 + 81 + 28 = 180
∠1 + 109 = 180
= 180 - 109
∠1 = 71
Problem 11 :
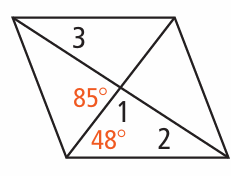
Solution :
∠3 = ∠2 (Alternate interior angles)
∠1 + 85 = 180 (linear pair)
∠1 = 180 - 85
∠1 = 95
Sum of interior angles of triangle = 180
95 + 48 + ∠2 = 180
143 + ∠2 = 180
∠2 = 180 - 143
∠2 = 37
Problem 12 :
ABCD is a parallelogram in which ∠DAB = 70o and ∠CBD = 55o. Find ∠CDB and ∠ADB.
Solution :
In parallelogram, opposite angels will be equal.
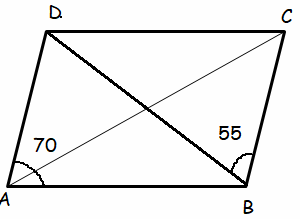
In triangle CDB,
∠CDB + ∠CBD + ∠DCB = 180
∠DCB = ∠DCB
∠CDB + 55 + 70 = 180
∠CDB + 125 = 180
∠CDB = 180 - 125
∠CDB = 55
∠ADB = 55 (alternate interior angles)
Problem 13 :
In a parallelogram ABCD, ∠A = (2x + 10)o and ∠C = (3x – 20)o. Find the value of x.
Solution :
In parallelogram ABCD, ∠A and ∠C are opposite angles and they must be equal.
2x + 10 = 3x - 20
2x - 3x = -20 - 10
-x = -30
x = 30
So, the value of x is 30
Problem 14 :
The sum of the two opposite angles of a parallelogram is 150o. Find all the angles of the parallelogram.
Solution :
Opposite angles will be equal in parallelogram and sum of adjacent angles will be add up to 180 degree.
One angle measure = 150/2
= 75
75 + adjacent angle = 180
adjacent angle = 180 - 75
= 105
So, the all four angles are 75, 75, 105 and 105.
Problem 15 :
If the angles of a quadrilateral are (x – 20)o, (x + 20)o, (x – 15)o and (x + 15)o, find x and the angles of the quadrilateral
Solution :
Sum of interior angles of quadrilateral = 360
(x – 20) + (x + 20) + (x – 15) + (x + 15) = 360
4x = 360
x = 360/4
x = 90
Applying the value of x, we get
x - 20 ==> 90 - 20 ==> 70
x + 20 ==> 90 + 20 ==> 110
x - 15 ==> 90 - 15 ==> 65
x + 15 ==> 90 + 15 ==> 105
So, the all four angles are 70, 110, 65 and 105.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling