GEOMETRY PROPERTIES OF PARALLELOGRAMS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Properties of Parallelogram
In parallelogram, opposite sides are parallel and equal.
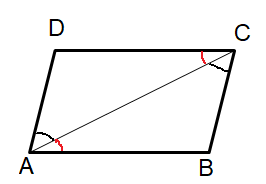
Here diagonal is like a transversal for parallel lines. Then alternate interior angles are equal.
That is,
∠DAC = ∠ACB, ∠DCA = ∠CAB
Since the opposite sides are parallel, we observe the same side interior angles.
∠DAB + ∠ADC = 180
∠DCB + ∠CBA = 180
Conclusion :
- Opposite sides are equal
- Opposite angles are equal
- Sum of consecutive interior angles will be 180 degree.
- Diagonals will bisect each other.
Problem 1 :
In the parallelogram shown below, find the value of x.
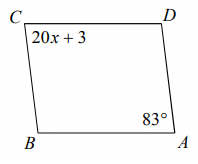
Opposite angles are equal.
20x + 3 = 83
20x = 83 - 3
20x = 80
x = 80/20
x = 4
Problem 2 :
Quadrilateral RSTU is a parallelogram. Find the values of x, y, a, and b.
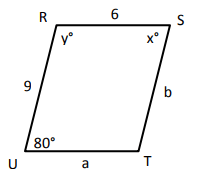
Solution :
Here some angles are missing and some side lengths is also missing.
In parallelogram, opposite sides are equal, opposite angles are equal and consecutive interior angles add upto 180 degree.
80 and y are consecutive interior angles.
80 + y = 180
y = 180 - 80
y = 100
x = 80 (opposite angles)
b = 9 and a = 6
Problem 3 :
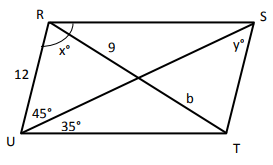
Solution :
y = 35
∠SRU + ∠RUT = 180
x + 45 + 35 = 180
x + 80 = 180
x = 180 - 80
x = 100
Problem 4 :
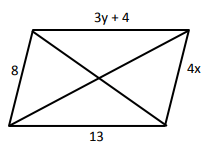
Solution :
Opposite sides are equal.
|
3y + 4 = 13 3y = 13 - 4 3y = 9 y = 9/3 y = 3 |
4x = 8 x = 8/4 x = 2 |
Problem 5 :
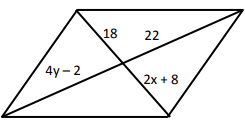
Solution :
Diagonals will bisect each other.
|
2x + 8 = 18 2x = 18 - 8 2x = 10 x = 10/2 x = 5 |
4y - 2 = 22 4y = 22 + 2 4y = 24 y = 24/4 y = 6 |
Problem 6 :
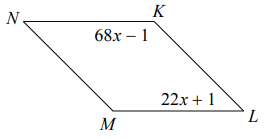
Solution :
Sum of consecutive angles = 180
68x - 1 + 22x + 1 = 180
90x = 180
x = 180 / 90
x = 2
Problem 7 :
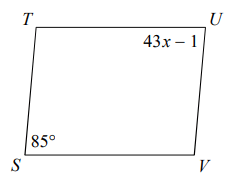
Solution :
∠TUV = ∠TSV
43x - 1 = 85
43x = 85 + 1
43x = 86
x = 86/43
x = 2
Problem 8 :
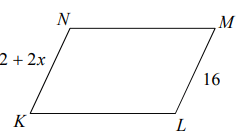
Solution :
MK = ML
2 + 2x = 16
2x = 16 - 2
2x = 14
x = 14/2
x = 7
Problem 9 :
Find angle F.
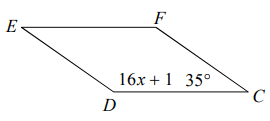
Solution :
Sum of consecutive angles = 180
16x + 1 + 35 = 180
16x + 36 = 180
16x = 180 - 36
16x = 144
x = 144/16
x = 9
∠F + ∠C = 180
∠F + 35 = 180
∠F = 180 - 35
∠F = 145
Problem 10 :
Find angle measure R.
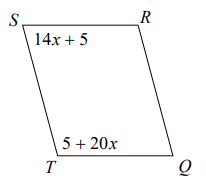
Solution :
Sum of consecutive angles = 180
14x + 5 + 5 + 20x = 180
34x + 10 = 180
34x = 180 - 10
34x = 170
x = 170/34
x = 5
Problem 11 :
In the diagram of the parking lot shown, m∠JKL = 60°, JK = LM = 21 feet, and KL = JM = 9 feet.
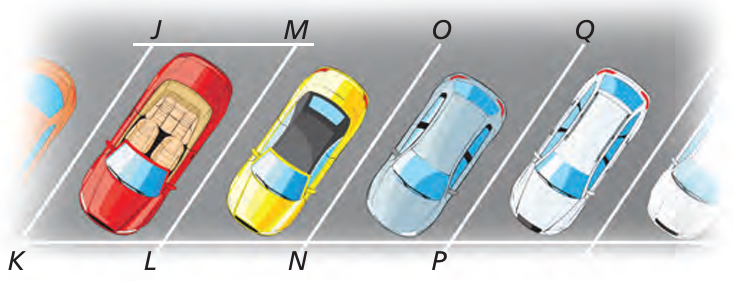
a) Explain how to show that parking space JKLM is a parallelogram.
b) Find m∠JML, m∠KJM, and m∠KLM.
c) LM || NO and NO || PQ . Which theorem could you use to show that JK II PQ ?
Solution :
a) Given that, JK = LM = 21 feet, and KL = JM = 9 feet
Since the opposite sides are equal, it must be a parallelogram.
b) Given that, m∠JML = 60
m∠JML = 60(Opposite angles are equal)
m∠KJM :
m∠KJM and m∠JML are co-interior angles. Then they add upto 180 degree.
m∠KJM = 180 - ∠JML
= 180 - 60
= 120
m∠KLM = 120 (since opposite angles are equal)
c) LM || NO and NO || PQ
Using transitive property of parallel line, we say that JK II PQ.
Problem 12 :
Describe how to prove that ABCD is a parallelogram.
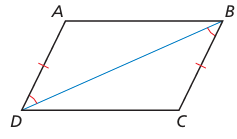
Solution :
In triangle ADB and triangle DCB,
∠DAB = ∠DBC
AD = BC (opposite sides)
DE = DB (Common)
Triangle ABD and triangle BDC are congruent.
Using CPCTC, AB = DC
Since opposite sides are equal, then it is a parallelogram.
Problem 13 :
Quadrilateral JKLM is a parallelogram. Describe how to prove that △MGJ ≅ △KHL.
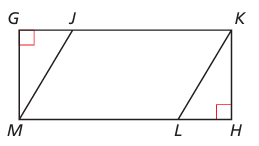
Solution :
In △MGJ and △KHL
∠MGJ = ∠KHL
JKLM is a parallelogram,
JM = KL
∠JML = ∠JKL (opposite angles in parallelogram)
∠MJK = ∠KLM (opposite angles in parallelogram)
∠GJM = 180 - ∠MJK
∠KLH = 180 - ∠KLH
∠GJM = ∠KLH
GM = KH
Using SAS, then △MGJ ≅ △KHL.
Problem 14 :
Three interior angle measures of a quadrilateral are 67°, 67°, and 113°. Is this enough information to conclude that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram? Explain your reasoning.
Solution :
Sum of angles in a quadrilateral = 360
Let x be the missing angle measure.
67 + 67 + 113 + x = 360
247 + x = 360
x = 360 - 247
x = 113
Since the opposite angles are equal, then it is parallelogram.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling