FINDING THE MISSING ANGLE OF A QUADRILATERAL
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
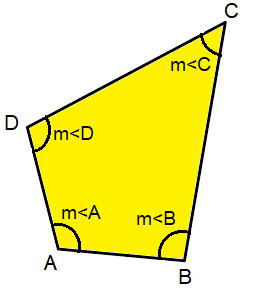
In the above figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
The sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
That is,
m ∠A + m ∠B + m ∠C + m ∠D = 360°
Find the measure of the indicated angle in each quadrilateral.
Problem 1 :
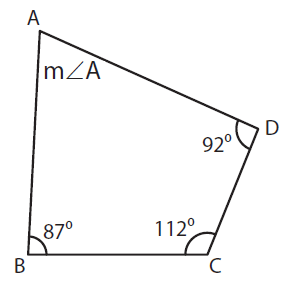
Solution :
The sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
m ∠A + m ∠B + m ∠C + m ∠D = 360°
Here m ∠B = 87°, m ∠C = 112°, and, m ∠D = 92°
m ∠A + 87° + 112° + 92° = 360°
m ∠A + 291° = 360°
m ∠A = 360° - 291°
m ∠A = 69°
Problem 2 :
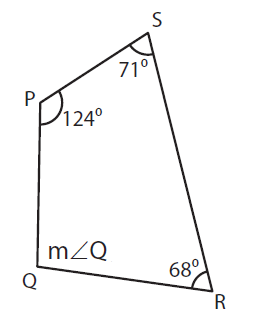
Solution :
The sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
m ∠P + m ∠Q + m ∠R + m ∠S = 360°
Here m ∠P = 124°, m ∠R = 68°, and, m ∠S = 71°
124° + m ∠Q + 68° + 71° = 360°
m ∠Q + 263° = 360°
m ∠Q = 360° - 263°
m ∠Q = 97°
Problem 3 :
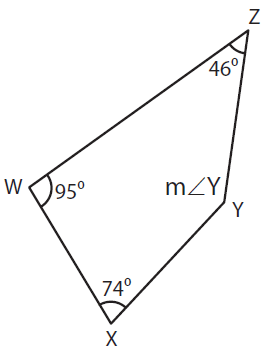
Solution :
The sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
m ∠W + m ∠X + m ∠Y + m ∠Z = 360°
Here m ∠W = 95°, m ∠X = 74°, and, m ∠Z = 46°
95° + 74° + m ∠Y + 46° = 360°
m ∠Y + 215° = 360°
m ∠Y = 360° - 215°
m ∠Y = 145°
Problem 4 :
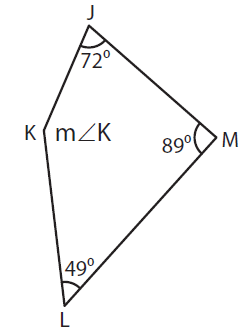
Solution :
The sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
m ∠J + m ∠K + m ∠L + m ∠M = 360°
Here m ∠J = 72°, m ∠L = 49°, and, m ∠M = 89°
72° + m ∠K + 49° + 89° = 360°
m ∠K + 210° = 360°
m ∠K = 360° - 210°
m ∠K = 150°
Problem 5 :
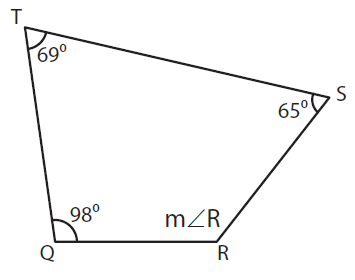
Solution :
m ∠Q + m ∠R + m ∠S + m ∠T = 360°
Here m ∠Q = 98°, m ∠S = 65°, and, m ∠T = 69°
98° + m ∠R + 65° + 69° = 360°
m ∠R + 232° = 360°
m ∠R = 360° - 232°
m ∠R = 128°
Problem 6 :
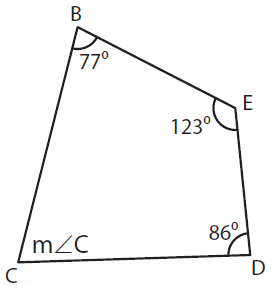
Solution :
m ∠B + m ∠C + m ∠D + m ∠E = 360°
Here m ∠B = 77°, m ∠D = 86°, and m ∠E = 123°
77° + m ∠C + 86° + 123° = 360°
m ∠C + 286° = 360°
m ∠C = 360° - 286°
m ∠C = 74°
Problem 7 :
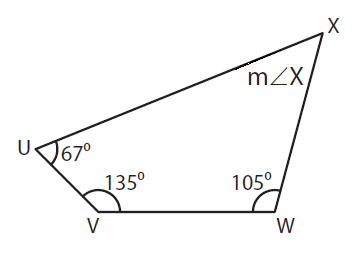
Solution :
m ∠U + m ∠V + m ∠W + m ∠X = 360°
Here m ∠U = 67°, m ∠V = 135°, and m ∠W= 105°
67° + 135° + 105° + m ∠X = 360°
m ∠X + 307° = 360°
m ∠X = 360° - 307°
m ∠X = 53°
Problem 8 :
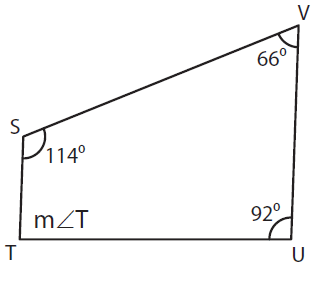
Solution :
m ∠S + m ∠T + m ∠U + m ∠V = 360°
Here m ∠S = 114°, m ∠U = 92°, and, m ∠V= 66°
114° + m ∠T + 92° + 66° = 360°
m ∠T + 272° = 360°
m ∠T = 360° - 272°
m ∠T = 88°
Problem 9 :
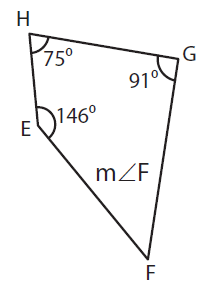
Solution :
m ∠E + m ∠F + m ∠G + m ∠H = 360°
Here m ∠E = 146°, m ∠G = 91°, and, m ∠H= 75°
146° + m ∠F + 91° + 75° = 360°
m ∠F + 312° = 360°
m ∠F = 360° - 312°
m ∠F = 48°
Problem 10 :
If three angles of a quadrilateral are each equal to 75°, the fourth angle is :-
(a) 150° (b) 135° (c) 45° (d) 75°
Solution :
In a quadrilateral, the sum of angles of quadrilateral = 360
Three angles of a quadrilateral = 75 degree. Let x be the fourth angle.
75 + 75 + 75 + x = 360
225 + x = 360
x = 360 - 225
x = 135
So, option b is correct.
Problem 11 :
What is the maximum number of obtuse angles that a quadrilateral can have ?
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Solution :
A quadrilateral can have a maximum of three obtuse angles. Since the sum of interior angles in any quadrilateral is 360 degrees, having four obtuse angles (each greater than 90 degrees) would result in a sum greater than 360, according to math sites
Problem 12 :
ABCD is a rhombus such that ∠ACB = 40°. Then ∠ADB is
(a) 40° (b) 45° (c) 50° (d) 60°
Solution :
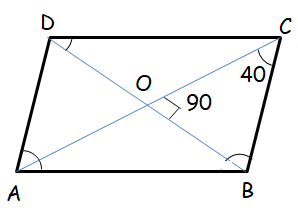
By observing the rhombus,
∠OAD = 40
∠AOD = 90
∠ADO = x
40 + 90 + x = 180
130 + x = 180
x = 180 - 130
x = 50
Problem 13 :
If PQRS is a parallelogram, then ∠P − ∠R is
(a) 90° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 0°
Solution :
So, ∠P = ∠R
Now, ∠P - ∠R = ∠P - ∠P
= 0
Therefore, the required value is 0.
Problem 14 :
ABCD is a square, diagonal AC is joined. Then the measurement of ∠ACB is
(a) 35° (b) 40° (c) 45° (d) 50°
Solution :
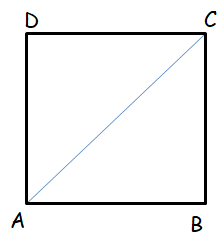
∠ACB = ∠BAC = 45 and ∠ABC = 90
∠ABC + ∠ACB + ∠BAC = 180
So, answer is option c.
Problem 15 :
In a parallelogram PQRS, if ∠P = (3x − 5)° and ∠Q = (2x + 15)°, then find the value of x.
Solution :
In a parallelogram PQRS,

sum of co-interior angles = 180 degree
∠P + ∠Q = 180
3x - 5 + 2x + 15 = 180
5x + 10 = 180
5x = 180 - 10
5x = 170
x = 170/5
x = 34
Problem 16 :
In the figure, ABCD is a rhombus. Find x & y
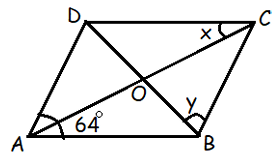
Solution :
x = 64° due to angle OAB and x being alternate interior angles.
Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors.
So, angle DAC and DCB would be 64 + 64= 128°.
So,in triangle COB, angle O = 90° and angle OCB = 64°.
90 + 64 + y = 180°(angle sum property)
154° + y = 180°
y = 180 - 154 = 26°
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling