FINDING EQUATION OF PARABOLA FROM GRAPH
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
If we have any of the following information is marked in the graph, we can find the equation of parabola easily.
i) Vertex and a point on the curve
ii) x-intercepts
iii) Any two points on the curve
Vertex form of parabola :
y = a(x - h)2 + k
Here (h, k) is vertex and (x, y) is one of the points of the curve.
Factored form of parabola :
y = a(x - p) (x - q)
Here p and q are x-intercepts of the parabola.
Find the equation of each of the following parabolas in the following forms.
i) Vertex form
ii) Standard form
Problem 1 :
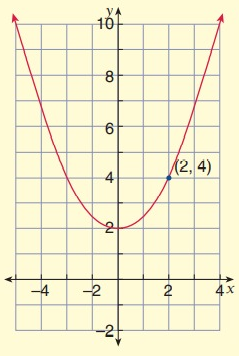
Solution:
Vertex Form:
Vertex form equation of a parabola that opens up with vertex (h, k)
y = a(x - h)2 + k
Vertex (h, k) = (0, 2)
Substitute x = 2 and y = 4 in equation,
4 = a(2 - 0)2 + 2 ----(1)
4 = a(4) + 2
4 = 4a + 2
4a = 2
a = 1/2
applying the value of a in (1)
By applying a = 1/2 in equation,
y = 1/2 (x - 0)2 + 2
y = 1/2 x2 + 2
Standard Form:
The parabola is open up with vertex at (0, 2).
Standard form equation of a parabola that opens up with vertex at (0, 2)
(x - h)2 = 4a(y - k)
Substitute x = 2 and y = 4 in equation,
(2 - 0)2 = 4a(4 - 2)
4 = 4a(2)
4 = 8a
a = 1/2
By applying a = 1/2 in equation
(x - 0)2 = 4(1/2)(y - 2)
x2 = 2(y - 2)
x2 = 2y - 4
x2 - 2y + 4 = 0
Problem 2 :
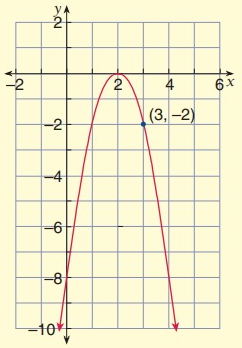
Solution:
Vertex form equation of a parabola that opens down with vertex (h, k)
y = a(x - h)2 + k
Vertex (h, k) = (2, 0)
Substitute x = 3 and y = -2 in equation,
-2 = a(3 - 2)2 + 0
-2 = a(1) + 0
a = -2
By applying a = -2 in equation,
y = -2(x - 2)2 + 0
Vertex form :
y = -2(x - 2)2
Standard Form:
y = -2(x - 2)2
y = -2 (x2 - 2x(2) + 22)
y = -2 (x2 - 4x + 4)
y = -2x2 + 8x - 8
Problem 3 :
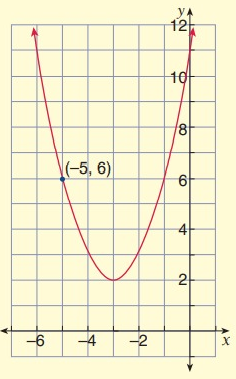
Solution:
Vertex form equation of a parabola that opens down with vertex (h, k)
y = a(x - h)2 + k
Vertex (h, k) = (-3, 2)
Substitute x = -5 and y = 6 in equation,
6 = a(-5 + 3)2 + 2
6 = a(4) + 2
6 = 4a + 2
4a = 4
a = 1
By applying a = 1 in equation,
y = 1 (x + 3)2 + 2
Vertex form :
y = (x + 3)2 + 2
Standard Form:
y = (x + 3)2 + 2
Expanding (x + 3)2 using algebraic identity, we get
y = x2 + 2x(3) + 32 + 2
y = x2 + 6x + 9 + 2
y = x2 + 6x + 11
Find the equations of parabolas shown in the following forms :
i) Intercept form
ii) Standard form
Problem 4 :
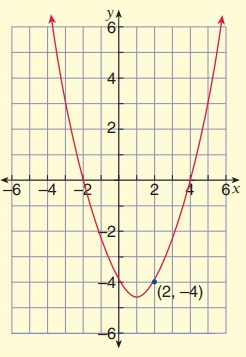
Solution:
Intercept Form:
Intercept form equation of the above parabola:
y = a(x - p) (x - q)
Because x-intercepts are (-2, 0) and (4, 0).
x = -2 ------> x + 2 = 0
x = 4 -------> x - 4 = 0
Then,
y = a(x + 2) (x - 4)
It passes through (2, -4). Substitute (x, y) = (2, -4)
-4 = a(2 + 2) (2 - 4)
-4 = a(4)(-2)
-4 = -8a
a = 1/2
Intercept form equation of the parabola:
y = 1/2(x + 2) (x - 4)
Standard form :
y = 1/2(x2 - 4x + 2x - 8)
y = 1/2(x2 - 2x - 8)
Problem 5 :
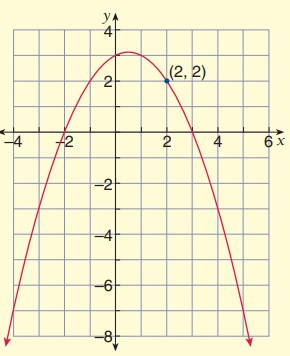
Solution:
Intercept Form:
Intercept form equation of the above parabola:
y = -a(x - p) (x - q)
Because x-intercepts are (-2, 0) and (3, 0).
x = -2 ------> x + 2 = 0
x = 3 -------> x - 3 = 0
Then,
y = -a(x + 2) (x - 3)
It passes through (2, 2). Substitute (x, y) = (2, 2)
2 = -a(2 + 2) (2 - 3)
2 = -a(4)(-1)
2 = 4a
a = 1/2
Intercept form equation of the parabola:
y = -1/2(x + 2) (x - 3)
Standard form :
y = -1/2(x2 - 3x + 2x - 6)
y = -1/2(x2 - x - 6)
Problem 6 :
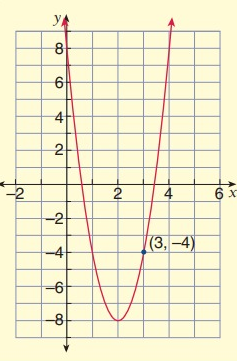
Solution:
Vertex Form:
Vertex form equation of a parabola that opens up with vertex (h, k)
y = a(x - h)2 + k
Vertex (h, k) = (2, -8)
Substitute x = 3 and y = -4 in equation,
-4 = a(3 - 2)2 - 8
-4 = a(1) - 8
-4 = a - 8
a = -4 + 8
a = 4
By applying a = 4 in equation,
y = 4 (x - 2)2 - 8
Standard Form:
y = 4 (x - 2)2 - 8
Expanding using algebraic identity, we get
y = 4 (x2 - 2x(2) + 22) - 8
y = 4(x2 - 4x + 4) - 8
y = 4x2 - 16x + 16 - 8
y = 4x2 - 16x + 8
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling