FIND VALUES OF TRIGONOEMTERIC FUNTIONS USING UNIT CIRCLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
What is unit circle ?
The unit circle is a circle with radius one.
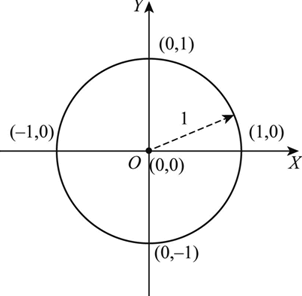
To find values of trigonometric functions using unit circle, we have to follow the given steps.
i) Identify the angle that lies in which quadrant.
ii) Find the reference angle if it is necessary, using the reference angle draw the triangle.
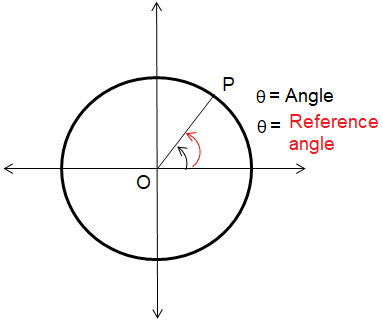 |
θ lies in 1st quadrant |
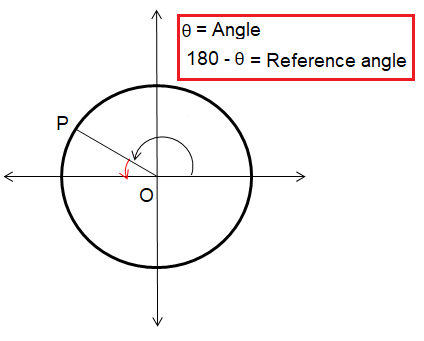 |
If θ lies in 2 nd quadrant |
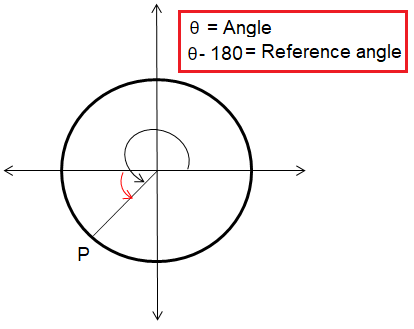 |
If θ lies in the third quadrant |
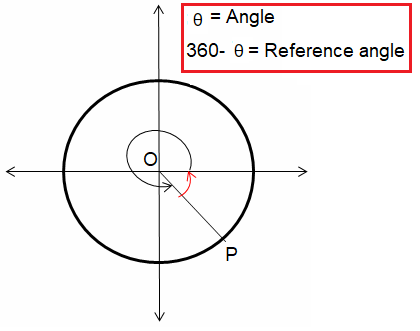 |
If θ lies in the fourth quadrant |
iii) Point p can be written in the form of (cos θ, sin θ)
iv) Using the concept of special right triangles, we can find values of trigonometric functions.
Solve the following problems using unit circle.
Example 1 :
cos (π/4)
Solution :
θ = π/4
0 ≤ θ ≤ π/2
θ lies in the first quadrant.
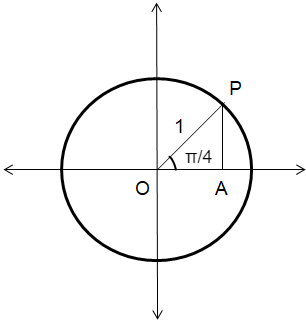
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 45, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 45
OP = √2 OA
1 = √2 OA
OA = 1/√2
OA = √2/2
cos θ = Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
cos (π/4) = OA/OP
= √2/2/1
cos (π/4) = √2/2
Example 2 :
cos 135
Solution :
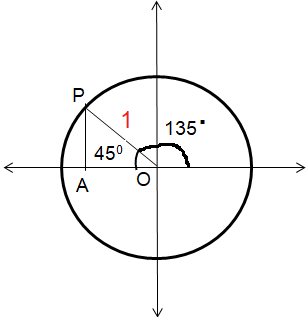
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 45, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 45
OP = √2 OA
1 = √2 OA
OA = 1/√2
OA = √2/2
Point P would be in the form of p(-x, y) ==> p(-OA, AP)
cos θ = Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
cos 135 = OA/OP
= -√2/2/1
cos 135 = -√2/2
Example 3 :
sin 5π/6
Solution :
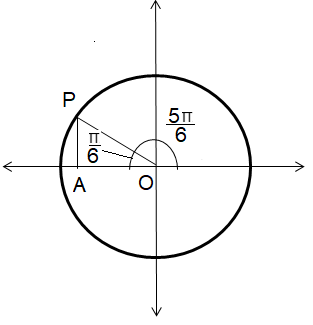
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 60, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 30
OP = 2 PA
1 = 2 PA
PA = 1/2
Point P would be in the form of p(-x, y) ==> p(-OA, AP)
sin θ = Opposite side / Hypotenuse
sin (5π/6) = PA/OP
= 1/2
sin (5π/6) = 1/2
Example 4 :
sin (-π/3)
Solution :
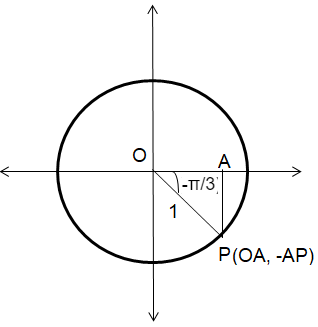
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 30, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 60
|
OP = 2 OA 1 = 2 OA OA = 1/2 |
AP = √3 OA AP = √3(1/2) AP = √3/2 |
Point P would be in the form of p(x, -y) ==> p(OA, -AP)
sin θ = Opposite side / Hypotenuse
sin (5π/6) = PA/OP
sin (-π/3) = -√3/2/1
sin (-π/3) = -√3/2
Example 5 :
tan 135
Solution :
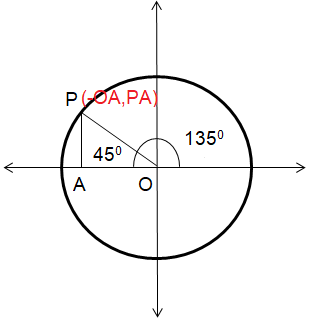
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 45, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 45
OP = √2 OA
1 = √2 OA
OA = 1/√2
OA = √2/2 = PA
Point P would be in the form of p(-x, y) ==> p(-OA, AP)
tan θ = Opposite side / Adjacent side
= -OA/OP
= -(√2/2) / (√2/2)
tan 135 = -1
Example 6 :
cos (-120)
Solution :
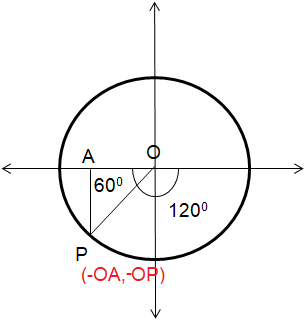
Triangle OPA is 30-60-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 30, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 60
OP = 2 OA
1 = 2 OA
OA = 1/2
Point P would be in the form of p(-x, y) ==> p(-OA, -AP)
cos θ = Adjacent side/hypotenuse
cos (-120) = OA/OP
= (-1/2)/1
cos (-120) = -1/2
Example 7 :
tan (3π/2)
Solution :
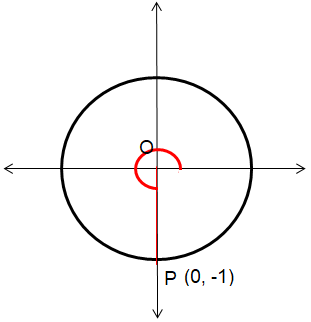
tan 3π/2 = sin 3π/2 / cos 3π/2
= -1/0
= undefined
Example 8 :
sin (-π/4)
Solution :
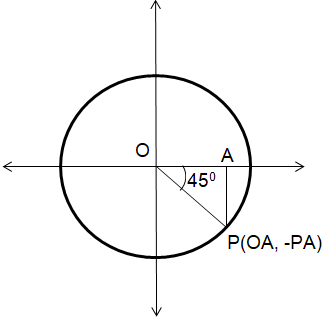
Triangle OPA is 45-45-90 special right triangle.
∠OPA = 45, ∠OAP = 90, ∠POA = 45
OP = √2 OA
1 = √2 OA
OA = 1/√2 = AP
Point P would be in the form of p(x, -y) ==> p(OA, -AP)
sin θ = Opposite side/hypotenuse
sin (-π/4) = OA/OP
= (-1/√2) / 1
= -1/√2
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling