EVALUATING WITH OPERATIONS ON FUNCTIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
There are many operations in between two functions.
- (f + g) (x) = f(x) + g(x)
- (f - g) (x) = f(x) - g(x)
- (f g) (x) = f(x) x g(x)
- (f /g) (x) = f(x) / g(x)
- (f∘g) (x) = f[g(x)]
Here we see some of the examples to show how to evaluate operation with functions.
Problem 1 :
Compute (f + g)(2), (f - g)(-1), (fg)(1/2), and (f/g)(0).
(a) f(x) = x2 - x, g(x) = 12 - x2
(b) f(x) = √(x + 3), g(x) = 2x - 1
Solution:
(a)
(f + g)(2) :
(f + g)(2) = f(2) + g(2)
f(2) = 22 - 2
= 2
g(2) = 12 - 22
= 8
f(2) + g(2) = 2 + 8
= 10
(f - g)(-1) :
(f - g)(-1) = f(-1) - g(-1)
f(-1) = (-1)2 - (-1)
= 2
g(-1) = 12 - (-1)2
= 11
f(-1) - g(-1) = 2 - 11
= -9
(fg)(1/2) :
(fg)(1/2) = f(1/2) ⋅ g(1/2)
f(1/2) = (1/2)2 - (1/2)
= -1/4
g(1/2) = 12 - (1/2)2
= 47/4
(f/g)(0) :
(f/g)(0) = f(0)/g(0)
f(0) = 0 - 0
= 0
g(0) = 12 - 0
= 12
(b)
(f + g)(2) :
(f + g)(2) = f(2) + g(2)
f(2) = √(2 + 3)
= √5
g(2) = 2(2) - 1
= 3
f(2) + g(2) = √5 + 3
(f - g)(-1) :
(f - g)(-1) = f(-1) - g(-1)
f(-1) = √(-1 + 3)
= √2
g(-1) = 2(-1) - 1
= -3
f(-1) - g(-1) = √2 + 3
(fg)(1/2) :
(fg)(1/2) = f(1/2) ⋅ g(1/2)
f(1/2) = √(1/2 + 3)
= √7/2
g(1/2) = 2(1/2) - 1
= 0
f(1/2) ⋅ g(1/2) = √7/2 ⋅ 0
= 0
(f/g)(0) :
(f/g)(0) = f(0)/g(0)
f(0) = √(0 + 3)
= √3
g(0) = 2(0) - 1
= -1
(c)
(f + g)(2) :
(f + g)(2) = f(2) + g(2)
f(2) = 2(2)
= 4
(f - g)(-1) :
(f - g)(-1) = f(-1) - g(-1)
f(-1) = 2(-1)
= -2
f(-1) - g(-1) = -2 + 1
= -1
(fg)(1/2) :
(fg)(1/2) = f(1/2) ⋅ g(1/2)
f(1/2) = 2(1/2)
= 1
(f/g)(0) :
(f/g)(0) = f(0)/g(0)
f(0) = 2(0)
= 0
(d)
(f + g)(2) :
(f + g)(2) = f(2) + g(2)
f(2) = 22
= 4
g(2) = 1/22
= 1/4
f(2) + g(2) = 4 + 1/4
= 17/4
(f - g)(-1) :
(f - g)(-1) = f(-1) - g(-1)
f(-1) = (-1)2
= 1
g(-1) = 1/(-1)2
= 1
(fg)(1/2) :
(fg)(1/2) = f(1/2) g(1/2)
f(1/2) = (1/2)2
= 1/4
f(1/2) g(1/2) = 1/4(4)
= 1
(f/g)(0) :
(f/g)(0) = f(0)/g(0)
f(0) = 0
g(0) = undefined
f(0)/g(0) = 0/undefined
= undefined
Problem 2 :
Use the table to state the domain of f(x) and g(x). Then find the following:
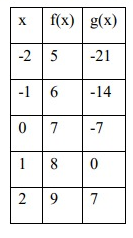
a. (f + g)(1)
b. (f/g)(0)
c. (f/g)(1)
d. f(-2) - g(2)
e. (2g + f)(-1)
Solution:
a.
(f + g)(1) = f(1) + g(1)
= 8 + 0
= 8
b.
(f/g)(0) = f(0)/g(0)
= 7/-7
= -1
c.
(f/g)(1) = f(1)/g(1)
= 8/0
= undefined
d.
= f(-2) - g(2)
= 5 - 7
= -2
e.
(2g + f)(-1) = 2g(-1) + f(-1)
= 2(-14) + 6
= -28 + 6
= -22
Problem 3 :
Let f(x) = x2 + 7x + 12 and g(x) = x2 - 9. State the domain if there are any restrictions.
a) Find (f + g)(x)
b) Find (2f - 3g)(x)
c) Find (fg)(x)
d) Find (f/g)(-2)
Solution:
a)
(f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)
= x2 + 7x + 12 + x2 - 9
= 2x2 + 7x + 3
= (2x + 1)(x + 3)
b)
(2f - 3g)(x) = 2f(x) - 3g(x)
= 2(x2 + 7x + 12) - 3(x2 - 9)
= 2x2 + 14x + 24 - 3x2 + 27
= -x2 + 14x + 51
= -(x - 17)(x + 3)
c)
(fg)(x) = f(x) g(x)
= (x2 + 7x + 12)(x2 - 9)
= x4 + 7x3 + 21x2 + 63x + 108
d)
(f/g)(-2) = f(-2)/g(-2)
f(-2) = (-2)2 + 7(-2) + 12
= 4 - 14 + 12
= 2
g(-2) = (-2)2 - 9
= 4 - 9
= -5
Problem 4 :
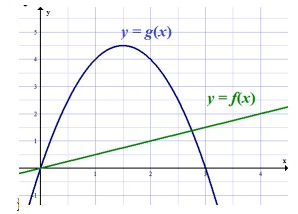
Use the graph to state the domain of f(x) and g(x). Then find the following.
a) (f + g)(1)
b) (fg)(1)
c) f(4) - g(2)
d) (2g + f)(3)
Solution:
a)
(f + g)(1) = f(1) + g(1)
= 0.5 + 4
= 4.5
b)
(fg)(1) = f(1) g(1)
= (0.5)(4)
= 2
c)
= f(4) - g(2)
= 2 - 4
= -2
d)
(2g + f)(3) = 2g(3) + f(3)
= 2(0) + 1.5
= 1.5
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling