EVALUATING EXPRESSIONS WITH NEGATIVE EXPONENTS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To evaluate an expression with exponents, we should to be aware of the rules of exponents.
The Required Rules of Exponents are below.
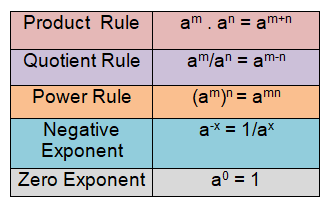
Example 1 :
yx1/3 ⋅ xy3/2
Solution :
= yx1/3 ⋅ xy3/2
By writing each term separately, we get
= y ⋅ x1/3 ⋅ x ⋅ y3/2
By combining the like terms, we get
= x1/3 ⋅ x ⋅ y3/2 ⋅ y
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= x1/3+1 ⋅ y3/2+1
= x4/3 ⋅ y5/2
So, the answer is x4/3 ⋅ y5/2
Example 2 :
4v2/3 ⋅ v-1
Solution :
= 4v2/3 ⋅ v-1
By writing each term separately, we get
= 4 ⋅ v2/3 ⋅ v-1
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= 4 ⋅ v2/3 - 1
= 4v-1/3
By using the negative exponent a-x = 1/ax
= (4)/v1/3
So, the answer is (4)/v1/3.
Example 3 :
(a1/2 b1/2)-1
Solution :
= (a1/2 b1/2)-1
By using the negative exponent a-x = 1/ax
= 1/(a1/2 b1/2)
So, the answer is 1/(a1/2 b1/2).
Example 4 :
(x0y1/3)3/2 x0
Solution :
= (x0y1/3)3/2 x0
By using the zero exponent a0 = 1, we get
= (1y1/3)3/2 1
= (y1/3)3/2
By using the power rule (am)n = amn, we get
= y(1/3 ⋅ 3/2)
= y3/6
= y1/2
So, the answer is y1/2.
Example 5 :
(2x1/2y1/3)/(2x4/3y-7/4)
Solution :
= (2x1/2y1/3)/(2x4/3y-7/4)
By writing each term separately, we get
= x1/2 ⋅ y1/3 ⋅ 1/x4/3 ⋅ 1/y-7/4
By combining the like terms, we get
= x1/2 ⋅ 1/x4/3 ⋅ y1/3 ⋅ 1/y-7/4
By using the quotient rule am/an = am-n, we get
= x1/2-4/3 ⋅ y1/3+7/4
= x-5/6⋅ y25/12
By using the negative exponent a-x = 1/ax
= y25/12 ⋅ 1/x5/6
= y25/12/x5/6
So, the answer is y25/12/x5/6.
Example 6 :
u-5/4v2 ⋅ (u3/2)-3/2
Solution :
= u-5/4v2 ⋅ (u3/2)-3/2
= u-5/4 ⋅ v2 ⋅ (u3/2)-3/2
By using the power rule (am)n = amn, we get
= u-5/4 ⋅ v2 ⋅ u(3/2 ⋅ (-3/2))
= u-5/4 ⋅ v2 ⋅ u-9/4
By combining the like terms, we get
= u-5/4 ⋅ u-9/4 ⋅ v2
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= u-5/4-9/4 ⋅ v2
= u-14/4 ⋅ v2
= u-7/2 ⋅ v2
By using the negative exponent a-x = 1/ax
= 1/u7/2 ⋅ v2
= v2/u7/2
So, the answer is v2/u7/2.
Example 7 :
uv ⋅ u ⋅ (v3/2)3
Solution :
= uv ⋅ u ⋅ (v3/2)3
= u ⋅ v ⋅ u ⋅ (v3/2)3
By using the power rule (am)n = amn, we get
= u ⋅ v ⋅ u ⋅ v9/2
By combining the like terms, we get
= u ⋅ u ⋅ v ⋅ v9/2
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= u1+1 ⋅ v1+9/2
= u2 ⋅ v11/2
So, the answer is u2 ⋅ v11/2.
Example 8 :
(2x-2y5/3)/x-5/4y-5/3 ⋅ xy1/2
Solution :
= (2x-2y5/3)/x-5/4y-5/3 ⋅ xy1/2
By writing each term separately, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-2y5/3 ⋅ 1/x-5/4 ⋅ 1/y-5/3 ⋅ 1/xy1/2
By using the negative exponent 1/a-x = ax, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-2y5/3 ⋅ x5/4 ⋅ y5/3 ⋅ 1/xy1/2
By using the negative exponent 1/ax = a-x, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-2y5/3 ⋅ x5/4 ⋅ y5/3 ⋅ x-1 ⋅ y-1/2
By combining the like terms, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-2 ⋅ x5/4 ⋅ x-1 ⋅ y5/3 ⋅ y5/3 ⋅ y-1/2
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-2+5/4 ⋅ x-1 ⋅ y5/3+5/3 ⋅ y-1/2
= 2 ⋅ x-3/4 ⋅ x-1 ⋅ y10/3 ⋅ y-1/2
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= 2 ⋅ x-3/4-1 ⋅ y10/3-1/2
= 2 ⋅ x-7/4 ⋅ y17/6
By using the negative exponent a-x = 1/ax
= 2 ⋅ y17/6 ⋅ 1/x7/4
= (2y17/6)/x7/4
So, the answer is (2y17/6)/x7/4.
Example 9 :
(a3/4b-1 ⋅ b7/4)/3b-1
Solution :
= (a3/4b-1 ⋅ b7/4)/3b-1
By writing each term separately, we get
= a3/4 ⋅ b-1 ⋅ b7/4 ⋅ 1/3 ⋅ b-1
By using the negative exponent 1/a-x = ax, we get
= a3/4 ⋅ b-1 ⋅ b7/4 ⋅ 1/3 ⋅ b
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= a3/4 ⋅ b-1+7/4 ⋅ 1/3 ⋅ b
= a3/4 ⋅ b3/4 ⋅ b ⋅ 1/3
= a3/4 ⋅ b3/4+1 ⋅ 1/3
= a3/4 ⋅ b7/4 ⋅ 1/3
= (a3/4b7/4)/3
So, the answer is (a3/4b7/4)/3.
Example 10 :
(3y-5/4)/y-1 ⋅ 2y-1/3
Solution :
= (3y-5/4)/y-1 ⋅ 2y-1/3
By writing each term separately, we get
= 3 ⋅ y-5/4 ⋅ 1/y-1 ⋅ 1/2 ⋅ 1/y-1/3
By using the negative exponent 1/a-x = ax, we get
= 3 ⋅ y-5/4 ⋅ y1 ⋅ 1/2 ⋅ y1/3
By using the product rule am ⋅ an = am+n, we get
= 3 ⋅ y-5/4+1 ⋅ 1/2 ⋅ y1/3
= 3 ⋅ y-1/4 ⋅ y1/3 ⋅ 1/2
= 3 ⋅ y-1/4+1/3 ⋅ 1/2
= 3 ⋅ y1/12 ⋅ 1/2
= (3y1/12)/2
So, the answer is (3y1/12)/2.
Example 11 :
If x3/5 = m and y-3/5 = n-1, which of the following is equal to xy ?
a) (mn)3/5 b) (mn)9/25 c) m5/3 n-5/3 d) (mn)5/3 e) n/m
Solution :
x3/5 = m and y-3/5 = n-1
x = m5/3 ---------(1)
y = (n-1)-5/3
y = n5/3 ---------(2)
xy = m5/3 [n5/3]
xy = (mn)5/3
Example 12 :
x4 x6/x8 = 81
According to the equation above, which of the following could equal to x2 ?
a) 81 b) 72 c) 18 d) 9 e) 3
Solution :
x4 x6/x8 = 81
x4 + 6 / x8 = 81
x10 / x8 = 81
x10 - 8 = 81
x2 = 81
So, the value of x2 is 81. Then option a is correct.
Example 13 :
If x6 = 60 and w10 = 20, what is x12 w-10 ?
a) 36 b) 60 c) 120 d) 180 e) 360
Solution :
x6 = 60 and w10 = 20
From x6 = 60, we raise power 2
(x6)2 = (60)2
x12 = (60)2
From w10 = 20, we raise power -1 we get
(w10)-1 = 20-1
w-10 = 20-1
w-10 = 1/20
x12 w-10 = (60)2(1/20)
= 3600/20
= 180
So, option d is correct.
Example 14 :
If a2 = b, what is a4 in terms of b ?
a) 2b b) b + 2 c) 2b + 2 d) b2 e) 4b
Solution :
a2 = b
Raising power 2 on both sides, we get
(a2)2 = b2
a4 = b2
So, option d is correct.
Example 15 :
If x3 = y9, what is x in terms of y ?
a) √y b) y2 c) y3 d) y6 e) y12
Solution :
x3 = y9
x = (y9)1/3
= y9/3
= y3
So, option c is correct.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling