CHARCTERISTICS OF ABSOLUTE VALUE FUNCTIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Every absolute value functions will have the following characteristics.
(i) Vertex
It is the minimum or maximum point of the absolute value function.
- If the curve opens up, it will have minimum.
- If the curve opens down, it will have maximum.
(ii) x - intercepts (roots, zeroes, solutions) and y - intercept
- The curve where it intersects the x axis is known as x intercept. To find x -intercept, we will replace y by 0.
- The curve where it intersects the y axis is known as y intercept. To find y-intercept, we will replace x by 0.
(iii) Slope and Reflections (or) Direction of opening
Absolute value functions will be in the form y = a|x-h| + k
Here a is slope,
- If it has positive slope, the curve will open up.
- If it has negative slope, the curve will open down.
(iv) Domain and Range
- The set of all possible inputs or values of x is known as domain. For absolute value functions all real values will be domain.
- The set of outputs is known as range.
(v) Increasing/decreasing interval
Based on the direction of opening, we can fix increasing or decreasing interval.
Find the following and graph it.
(i) Vertex
(ii) Slope
(iii) y-intercept and x-intercept
(iv) domain and range
(v) Increasing and decreasing interval.
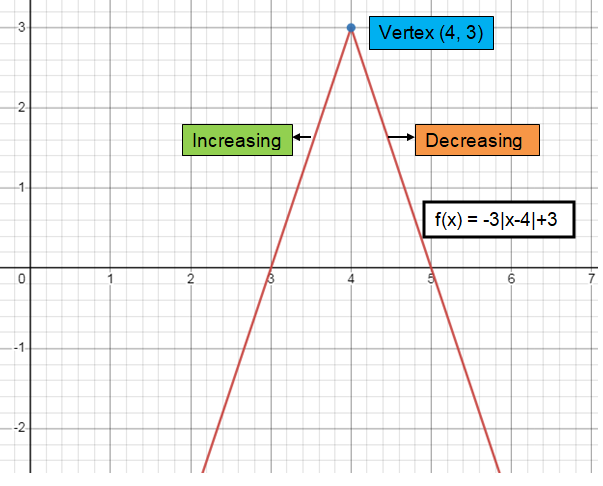
Problem 1 :
f(x) = -3│x - 4│ + 3
Solution :
a = -3, h = 4, k = 3
Vertex:
f(x) = -3│x - 4│ + 3
Comparing with f(x) = a |x - h|+ k
Vertex (h, k) = (4, 3)
Slope :
Slope (a) = -3
The curve will open down.
y- intercept :
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = -3│0 - 4│ + 3
y = -3(4) + 3
y = -12 + 3
y = -9
y- Intercept is (0, -9)
Zeros :
x- Intercept, put y = 0
-3│x - 4│ + 3 = 0
-3│x - 4│= -3
│x - 4│= -3/-3
│x - 4│= 1
x = 1 + 4
x = 5
x- Intercept is (5, 0)
Domain and range :
- All real value is domain.
- Range is [3, -∞)
Increasing and decreasing :
- To the left of maximum, it is increasing. (-∞, 4)
- To the right of maximum, it is decreasing. (4, ∞)
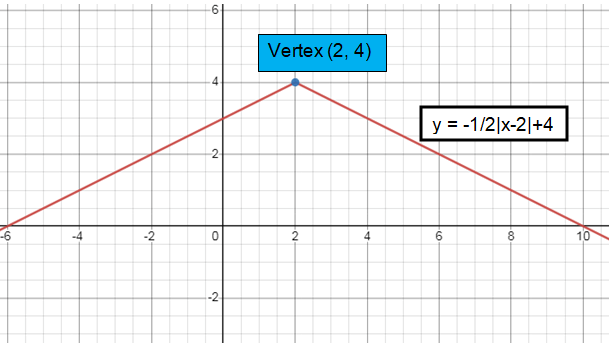
Problem 2 :
f(x) = -1/2│x - 2│ + 4
Solution :
a = -1/2, h = 2, k = 4
Vertex :
f(x) = -1/2│x - 2│ + 4
Comparing with f(x) = a│x - h│+ k
Vertex (h, k) = (2, 4)
Slope :
Slope (a) = -1/2
The curve will open down.
y- intercept :
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = -1/2│0 - 2│ + 4
y = -1/2(2) + 4
y = -1 + 4
y = 3
y- Intercept = (0, 3)
Zeros :
x- Intercept, put y = 0
-1/2│x - 2│ + 4 = 0
-1/2│x - 2│= -4
│x - 2│= -4(-2)
│x - 2│= 8
x = 8 + 2
x = 10
x- Intercept is (10, 0)
Domain and range:
- All real value is domain.
- Range is (-∞, 4]
Increasing and decreasing:
- To the left of maximum, it is increasing. (-∞, 2]
- To the right of maximum, it is decreasing. [2, ∞)
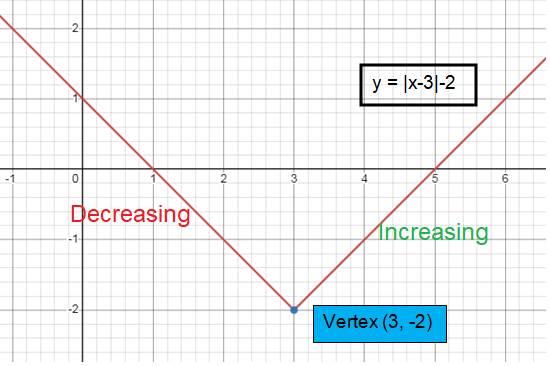
Problem 3 :
f(x) = │x - 3│ - 2
Solution :
a = 1, h = 3, k = -2
Vertex :
f(x) = │x - 3│ - 2
Comparing with f(x) = a│x - h│+ k
Vertex (h, k) is (3, -2)
Slope :
Slope (a) = 1
The curve will open up.
y- intercept :
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = │0 - 3│ - 2
y = 3 - 2
y = 1
y- Intercept is (0, 1)
Zeros :
x- Intercept, put y = 0
│x - 3│ - 2 = 0
│x - 3│= 2
x = 2 + 3
x = 5
x- Intercept is (5, 0)
Domain and range :
- All real value is domain.
- Range is [-2, ∞)
Increasing and decreasing :
- To the right of minimum, it is increasing. (∞, 3]
- To the left of minimum, it is decreasing. [3,-∞)
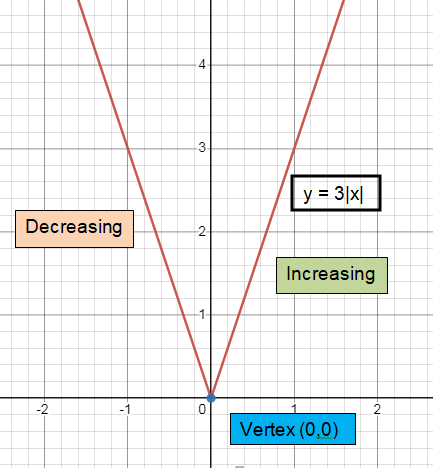
Problem 4 :
f(x) = 3│x│
Solution :
a = 3, h = 0, k = 0
Vertex:
f(x) = 3│x - 0│ + 0
Comparing with f(x) = a│x - h│+ k
Vertex (h, k) = (0, 0)
Slope:
Slope (a) = 3
The curve will open up.
y- intercept:
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = 3(0)
y = 0
y- Intercept = (0, 0)
Zeros:
x- Intercept, put y = 0
3│x│ = 0
x = 0
x- Intercept = (0, 0)
Domain and range:
- All real value is domain.
- Range is [0, ∞)
Increasing and decreasing:
- To the right of minimum, it is increasing. [0, ∞)
- To the left of minimum, it is decreasing. (-∞, 0]
Problem 5 :
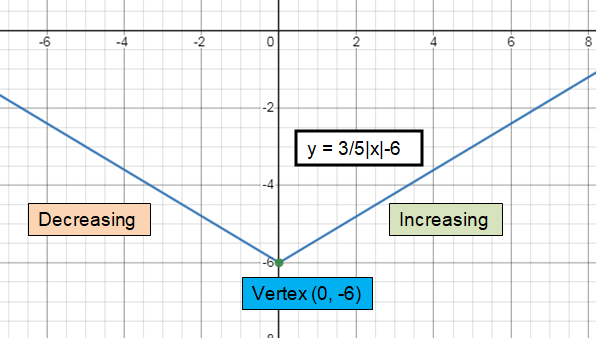
y = 3/5 │x│- 6
Solution :
a = 3/5, h = 0, k = -6
Vertex :
f(x) = 3/5│x - 0│ - 6
Comparing with f(x) = a│x - h│+ k
Vertex (h, k) = (0, -6)
Slope :
Slope (a) = 3/5
The curve will open up.
y- intercept :
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = 3/5(0) - 6
y = -6
y- Intercept is (0, -6)
Zeros :
x- Intercept, put y = 0
3/5│x│- 6 = 0
3/5 │x│ = 6
x = 10
x- Intercept is (10, 0)
Domain and range :
- All real value is domain.
- Range is [-6, ∞)
Increasing and decreasing:
- To the right of minimum, it is increasing. (0, ∞)
- To the left of minimum, it is decreasing. (-∞, 0)
Problem 6 :
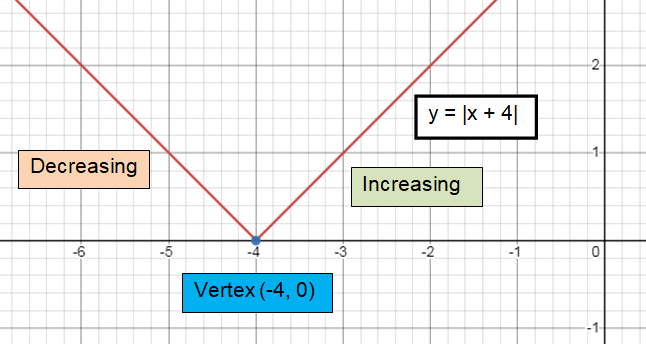
y =│x + 4│
Solution :
a = 1, h = -4, k = 0
Vertex:
f(x) =│x + 4│ + 0
Comparing with f(x) = a│x - h│+ k
Vertex (h, k) is (-4, 0)
Slope:
Slope (a) = 1
The curve will open up.
y- intercept:
y- Intercept, put x = 0
y = │0 + 4│
y = 4
y- Intercept = (0, 4)
Zeros:
x- Intercept, put y = 0
│x + 4│= 0
x = -4
x- Intercept = (-4, 0)
Domain and range:
- All real value is domain.
- Range is [0, ∞)
Increasing and decreasing:
- To the right of minimum, it is increasing. (-4, ∞)
- To the left of minimum, it is decreasing. (-∞, -4)
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling